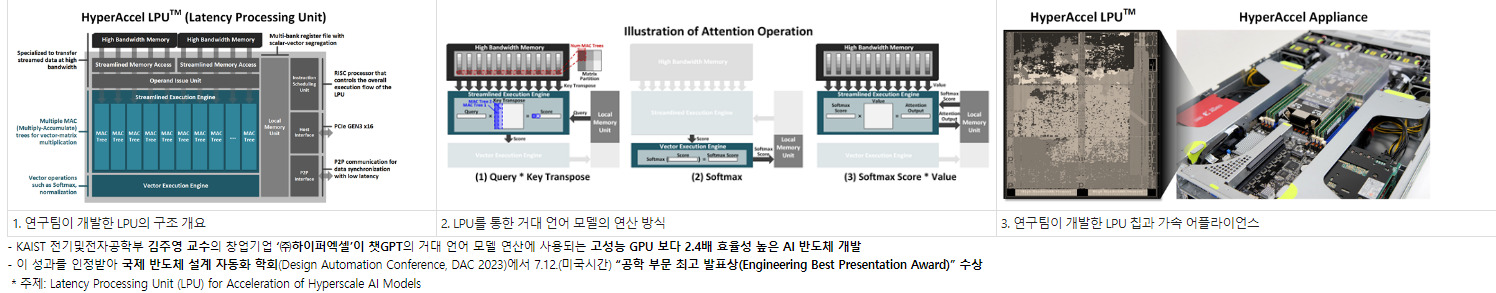
Myeonggu Kang; Hyein Shin; Junkyum Kim; Lee-Sup Kim, “ MGen: A Framework for Energy-Efficient In-ReRAM Acceleration of Multi-Task BERT,” IEEE Transactions on Computers ( Volume: 72, Issue: 11, November 2023)
Abstract: Recently, multiple transformer models, such as BERT, have been utilized together to support multiple natural language processing (NLP) tasks in a system, also known as multi-task BERT. Multi-task BERT with very high weight parameters increases the area requirement of a processing in resistive memory (ReRAM) architecture, and several works have attempted to address this model size issue. Despite the reduced parameters, the number of multi-task BERT computations remains the same, leading to massive energy consumption in ReRAM-based deep neural network (DNN) accelerators. Therefore, we suggest a framework for better energy efficiency during the ReRAM acceleration of multi-task BERT. First, we analyze the inherent redundancies of multi-task BERT and the computational properties of the ReRAM-based DNN accelerator, after which we propose what is termed the model generator, which produces optimal BERT models supporting multiple tasks. The model generator reduces multi-task BERT computations while maintaining the algorithmic performance. Furthermore, we present task scheduler, which adjusts the execution order of multiple tasks, to run the produced models efficiently. As a result, the proposed framework achieves maximally 4.4× higher energy efficiency over the baseline, and it can also be combined with the previous multi-task BERT works to achieve both a smaller area and higher energy efficiency.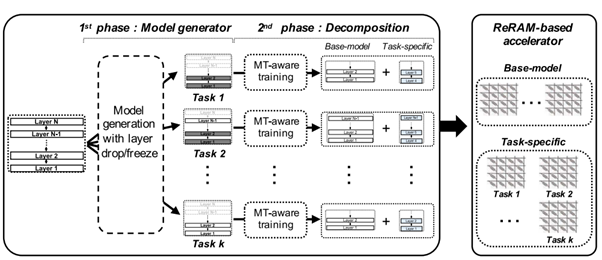
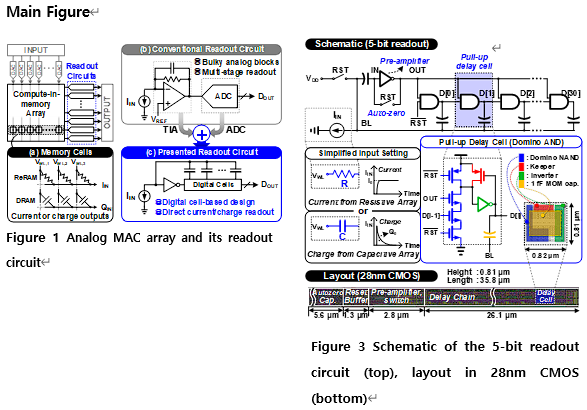
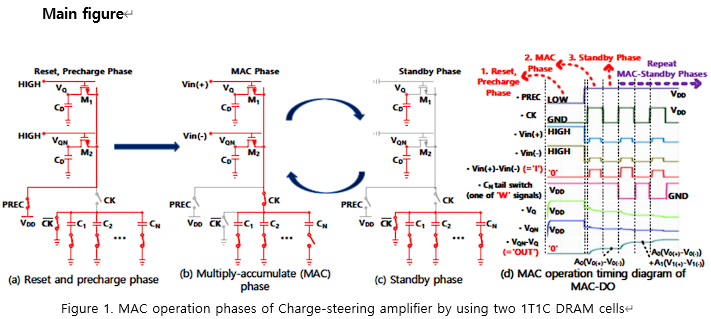
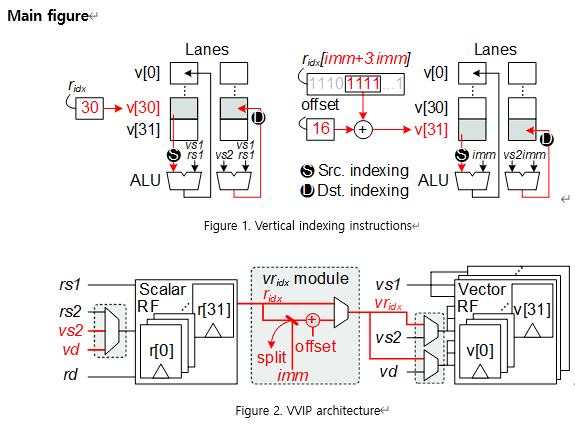 s, and 1.2 times average performance improvement in unstructured sparse point-wise convolution tasks when compared to conventional control sequences.
s, and 1.2 times average performance improvement in unstructured sparse point-wise convolution tasks when compared to conventional control sequences.