Shinhwan Kang, Kyuhan Lee, and Kijung Shin
PAKDD 2022: Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining 2022
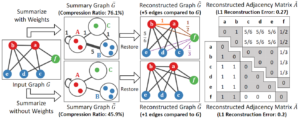
Abstract: Which one is better between two representative graph summarization models with and without edge weights? From web graphs to online social networks, large graphs are everywhere. Graph summarization, which is an effective graph compression technique, aims to find a compact summary graph that accurately represents a given large graph. Two versions of the problem, where one allows edge weights in summary graphs and the other does not, have been studied in parallel without direct comparison between their underlying representation models. In this work, we conduct a systematic comparison by extending three search algorithms to both models and evaluating their outputs on eight datasets in five aspects: (a) reconstruction error, (b) error in node importance, (c) error in node proximity, (d) the size of reconstructed graphs, and (e) compression ratios. Surprisingly, using unweighted summary graphs leads to outputs significantly better in all the aspects than using weighted ones, and this finding is supported theoretically. Notably, we show that a state-of-the-art algorithm can be improved substantially (specifically, 8.2X, 7.8X, and 5.9X in terms of (a), (b), and (c), respectively, when (e) is fixed) based on the observation.