Authors: Seyeon Kim (KAIST), Kyungmin Bin (SNU), Sangtae Ha (CU Boulder), Song Chong (KAIST)
Abstract:
DVFS(dynamic voltage and frequency scaling) is a system-level technique that adjusts voltage and frequency levels of CPU/GPU at runtime to balance energy efficiency and high performance. DVFS has been studied for many years, but it is considered still challenging to realize a DVFS that performs ideally for mobile devices for two main reasons: i) an optimal power budget distribution between CPU and GPU in a power-constrained platform can only be defined by the application performance, but conventional DVFS implementations are mostly application-agnostic; ii) mobile platforms experience dynamic thermal environments for many reasons such as mobility and holding methods, but conventional implementations are not adaptive enough to such environmental changes. In this work, we propose a deep reinforcement learning-based frequency scaling technique, zTT. zTT learns thermal environmental characteristics and jointly scales CPU and GPU frequencies to maximize the application performance in an energy-efficient manner while achieving zero thermal throttling. Our evaluations for zTT implemented on Google Pixel 3a and NVIDIA JETSON TX2 platform with various applications show that zTT can adapt quickly to changing thermal environments, consistently resulting in high application performance with energy efficiency. In a high-temperature environment where a rendering application with the default mobile DVFS fails to keep producing more than a target frame rate, zTT successfully manages to do so even with 23.9% less average power consumption.
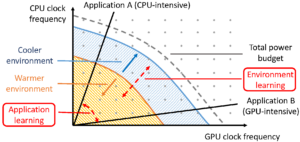
<The purpose and impact of learning in zTT>
(Figure) Figure illustrates the purpose and impact of learning in zTT. The lattice points within the total power budget curve for a mobile device represent all available CPU/GPU power consumption combinations. The graph shows that the better the cooling, the more combinations are usable, thus providing better performance for an application. To find out the best possible combination at the moment, zTT learns the environment and application performance.