Title: NAND-Net: Minimizing Computational Complexity of In-Memory Processing for Binary Neural Networks
Authors: Hyeon-Uk Kim, Jae-Hyeong Sim, Yeong-Jae Choi, Lee-Sup Kim
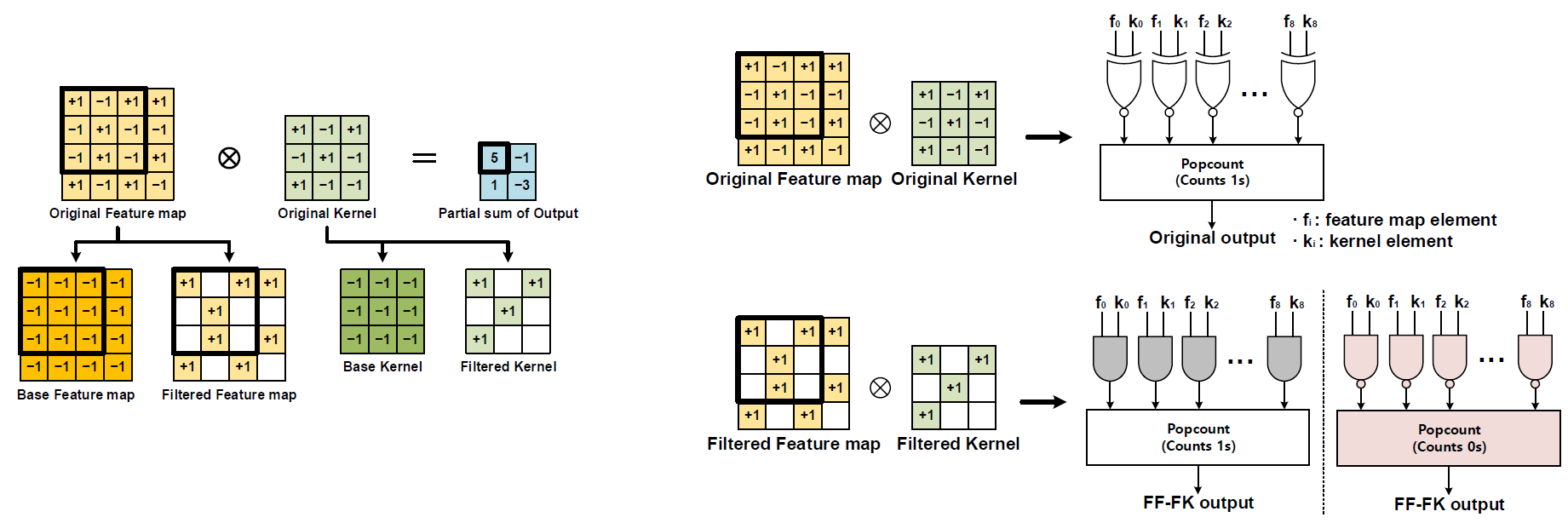
Popular deep learning technologies suffer from memory bottlenecks, which significantly degrade the energy-efficiency, especially in mobile environments. In-memory processing for binary neural networks (BNNs) has emerged as a promising solution to mitigate such bottlenecks, and various relevant works have been presented accordingly. However, their performances are severely limited by the overheads induced by the modification of the conventional memory architectures. To alleviate the performance degradation, we propose NAND-Net, an efficient architecture to minimize the computational complexity of in-memory processing for BNNs. Based on the observation that BNNs contain many redundancies, we decomposed each convolution into sub-convolutions and eliminated the unnecessary operations. In the remaining convolution, each binary multiplication (bitwise XNOR) is replaced by a bitwise NAND operation, which can be implemented without any bit cell modifications. This NAND operation further brings an opportunity to simplify the subsequent binary accumulations (popcounts). We reduced the operation cost of those popcounts by exploiting the data patterns of the NAND outputs. Compared to the prior state-of-the-art designs, NAND-Net achieves 1.04-2.4x speedup and 34-59% energy saving, thus making it a suitable solution to implement efficient in-memory processing for BNNs.
Title: An Optimized Design Technique of Low-bit Neural Network Training for Personalization on IoT Devices
Authors: Seung-Kyu Choi, Jae-Kang Shin, Yeong-Jae Choi, and Lee-Sup Kim
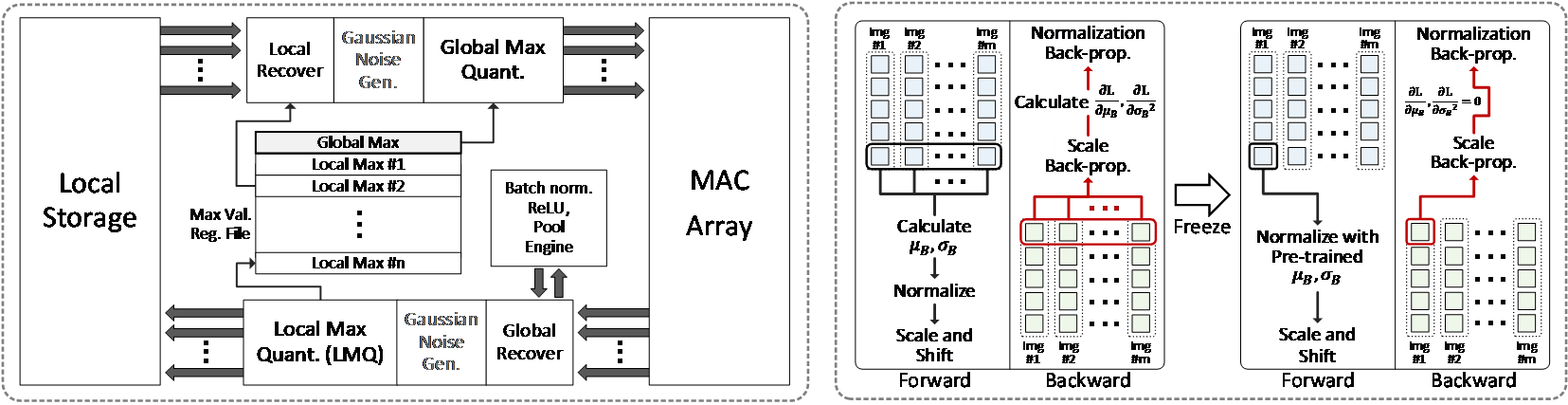
Personalization by incremental learning has become essential for IoT devices to enhance the performance of the deep learning models trained with global datasets. To avoid massive transmission traffic in the network, exploiting on-device learning is necessary. We propose a software/hardware co-design technique that builds an energy-efficient low-bit trainable system: (1) software optimizations by local low-bit quantization and computation freezing to minimize the on-chip storage requirement and computational complexity, (2) hardware design of a bit-flexible multiply-and-accumulate (MAC) array sharing the same resources in inference and training. Our scheme saves 99.2% on on-chip buffer storage and achieves 12.8x higher peak energy efficiency compared to previous trainable accelerators.
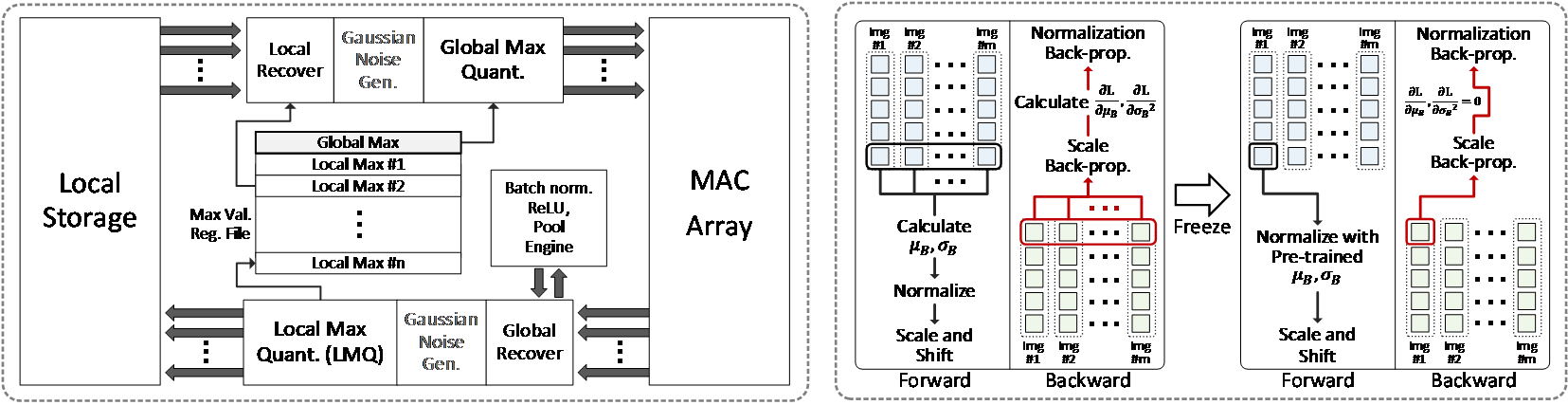
Figure 1. Optimizations to operate multiply-and-accumulate for CNN training in fixed-point based MAC units

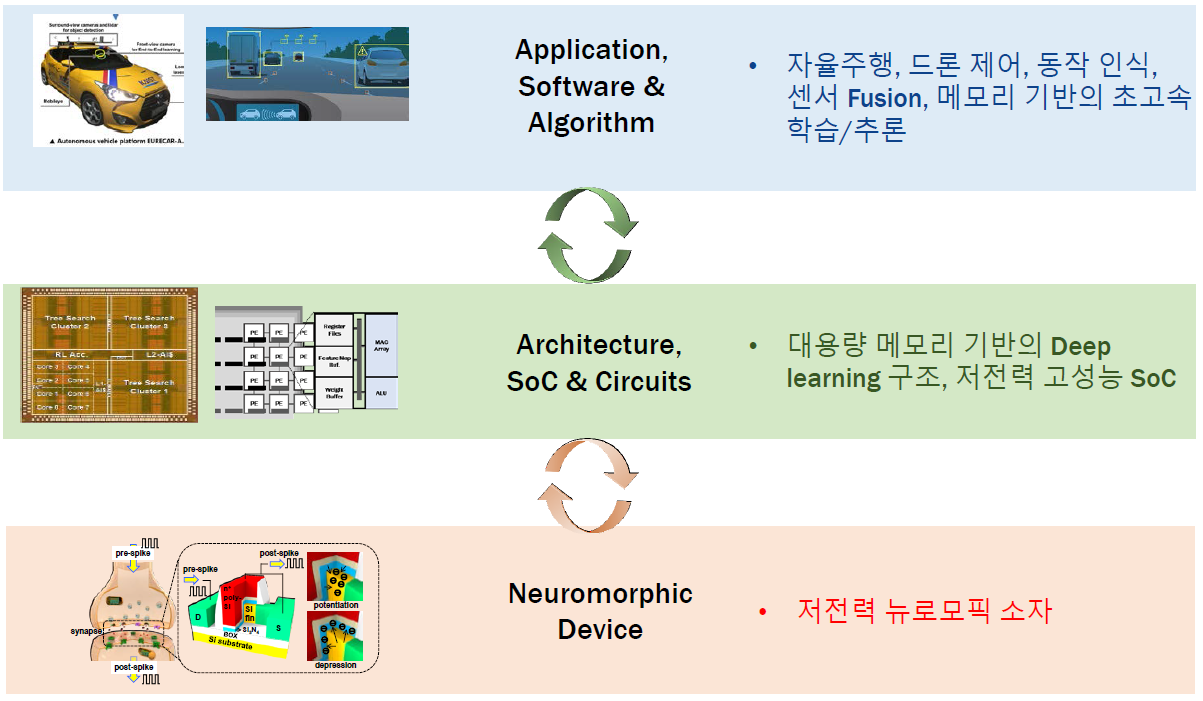
SK하이닉스와 KAIST는 2018년 11월 30일 대전 KAIST 본원에서 ‘차세대 인공지능 반도체 시스템 연구 센터’ 협약식을 가졌습니다. (센터장: 조성환 교수).
차세대 인공지능 반도체 시스템 연구 센터는 4차 산업 혁명을 대비하는 인공지능 반도체 시스템 개발을 목표로 SK하이닉스와 KAIST의 센서, 알고리즘, 머신러닝 SoC 및 소자 분야 10개 연구실의 전문 인력이 공동으로 참여할 계획입니다.
SK하이닉스와 KAIST는 개소식에서 인공지능에 최적화된 새로운 반도체 소자 개발, 머신러닝 가속기 칩 개발, 자동차 및 드론 등의 자율주행으로의 응용 기술 개발을 골자로 하는 세부 연구 계획을 공유하였으며, 센터의 공동 운영을 통해 연구 인력 상호 교류 및 교육 등을 통한 협력체계도 구축할 예정입니다.
이번 협약식을 통해 SK하이닉스는 메모리 분야의 탄탄한 입지를 바탕으로 KAIST와 더불어 4차 산업혁명에 따른 비메모리 분야의 핵심 기술 개발을 선도하여 새로운 시장 개척을 도모하는 계기를 마련하게 되었습니다.
본 센터 설립은 인공지능 분야의 체계적인 기술 개발과 전문 인력 양성 측면에서 국내 학계와 산업계에 모두 도움이 될 것으로 기대됩니다.