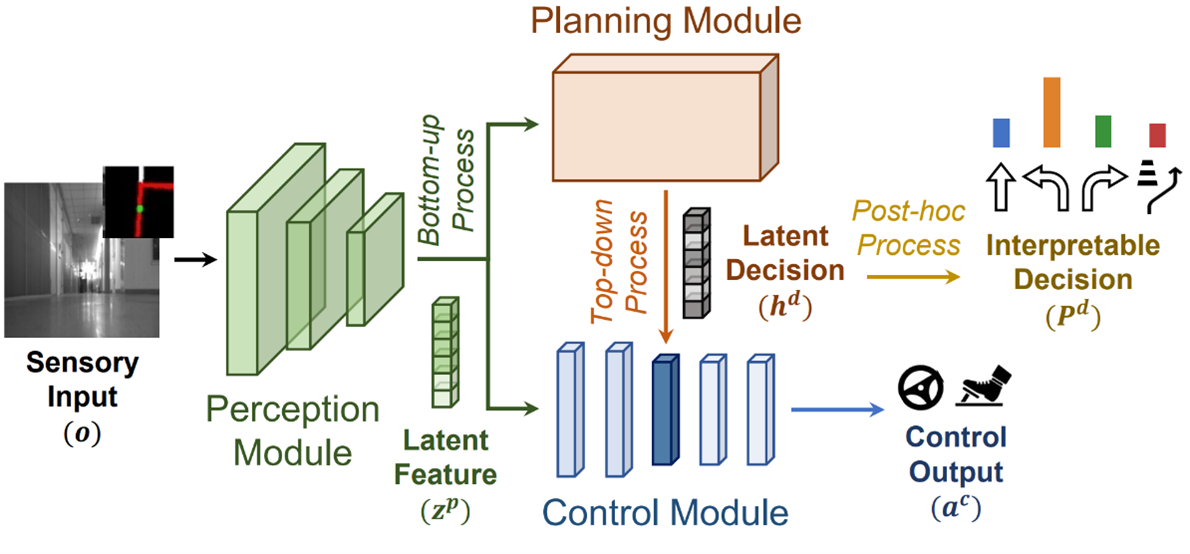
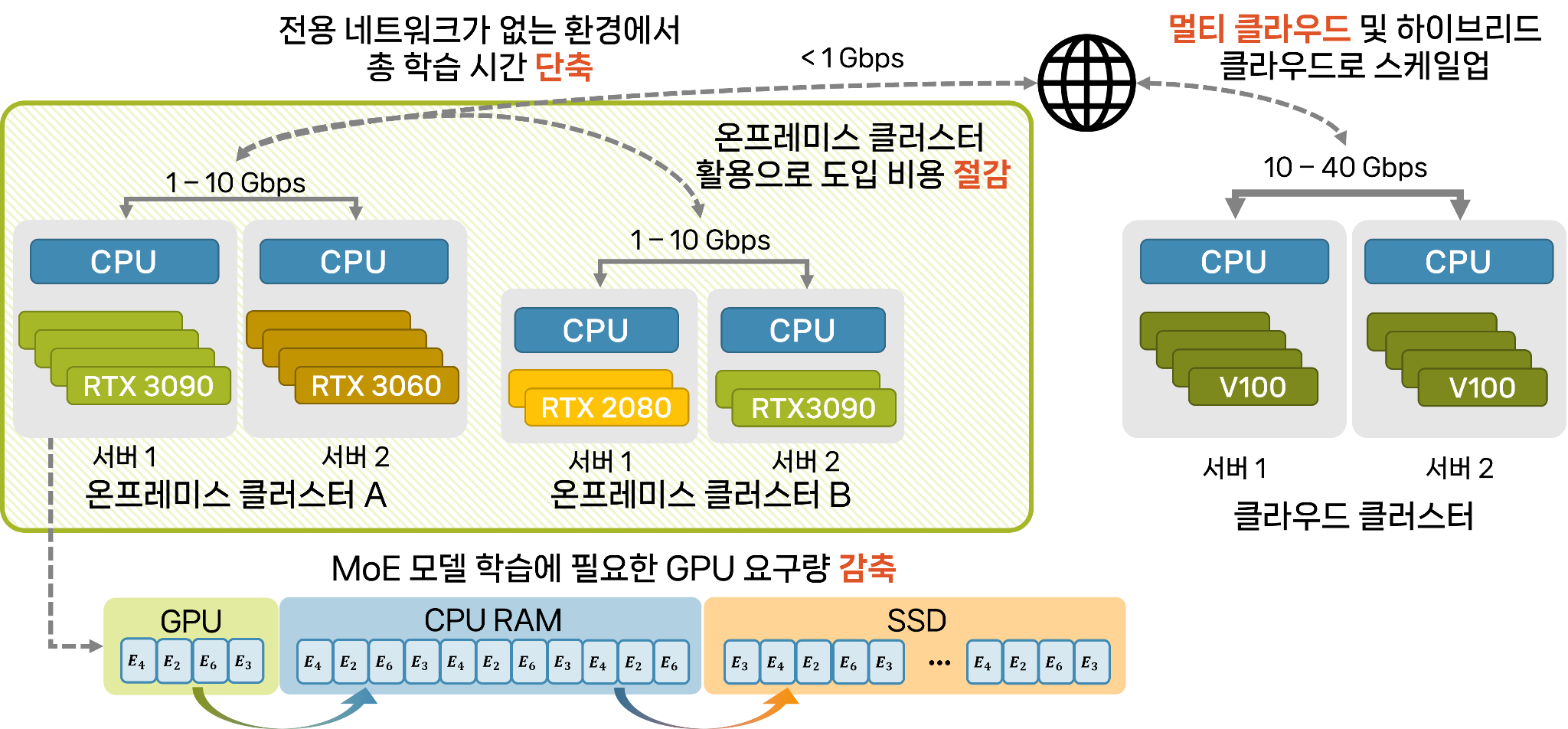
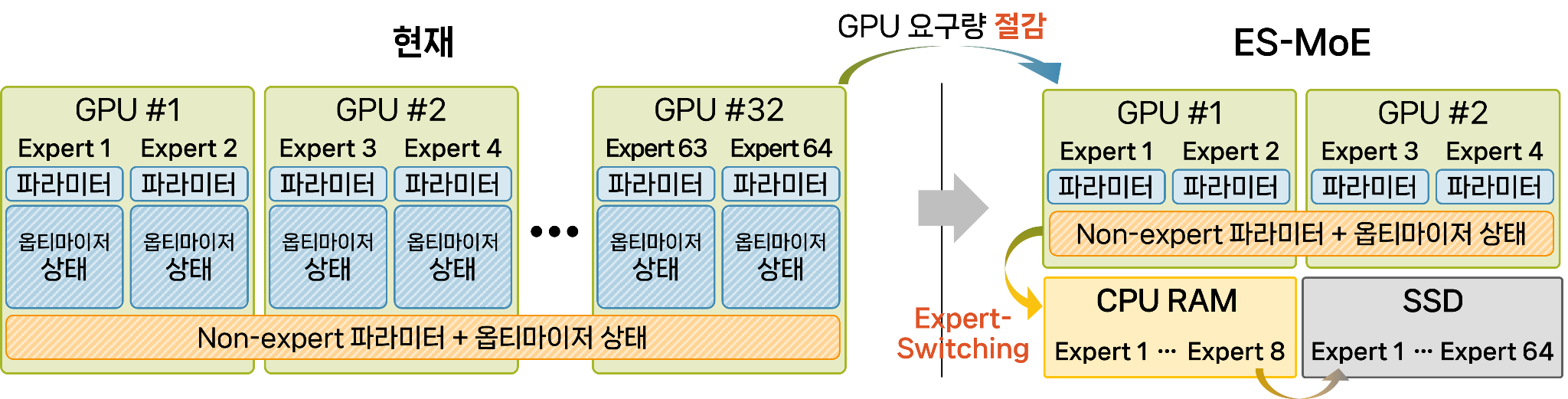
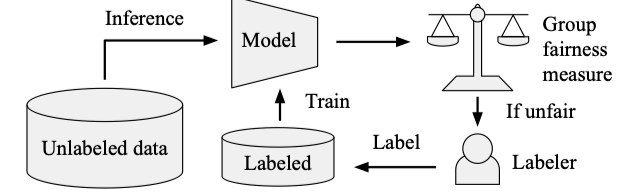
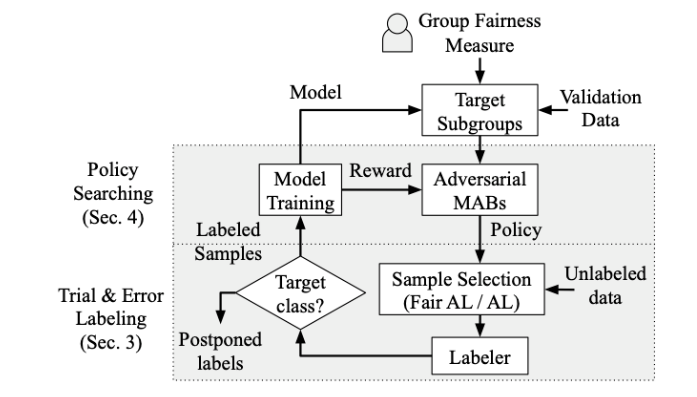
Abstract: We introduce MoNet, a novel functionally modular network for self-supervised and interpretable end-to-end learning. By leveraging its functional modularity with a latent-guided contrastive loss function, MoNet efficiently learns task-specific decision-making processes in latent space without requiring task-level supervision. Moreover, our method incorporates an online, post-hoc explainability approach that enhances the interpretability of end-to-end inferences without compromising sensorimotor control performance. In real-world indoor environments, MoNet demonstrates effective visual autonomous navigation, outperforming baseline models by 7% to 28% in task specificity analysis. We further explore the interpretability of our network through post-hoc analysis of perceptual saliency maps and latent decision vectors. This provides valuable insights into the incorporation of explainable artificial intelligence into robotic learning, encompassing both perceptual and behavioral perspectives. Supplementary materials are available at https://sites.google.com/view/monet-lgc.
Main Figure: