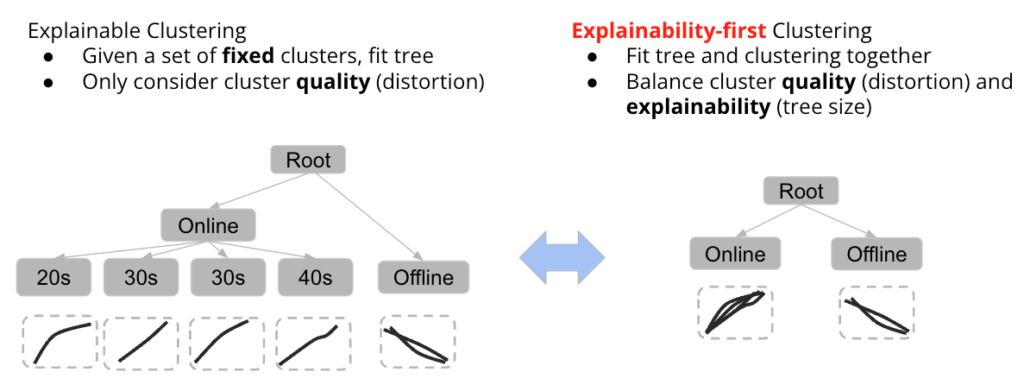
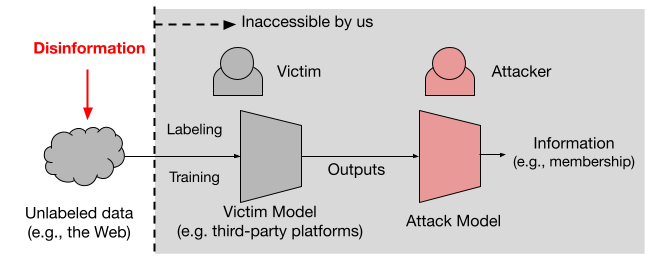
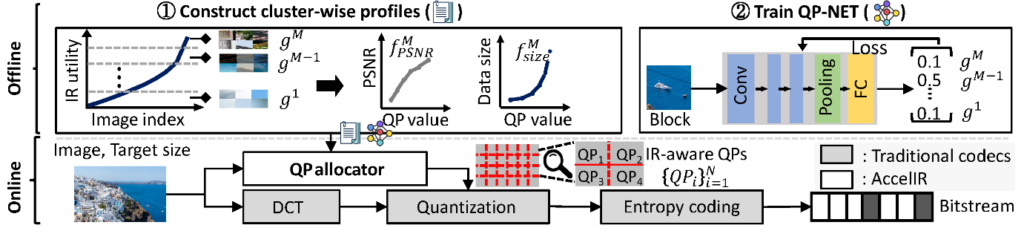
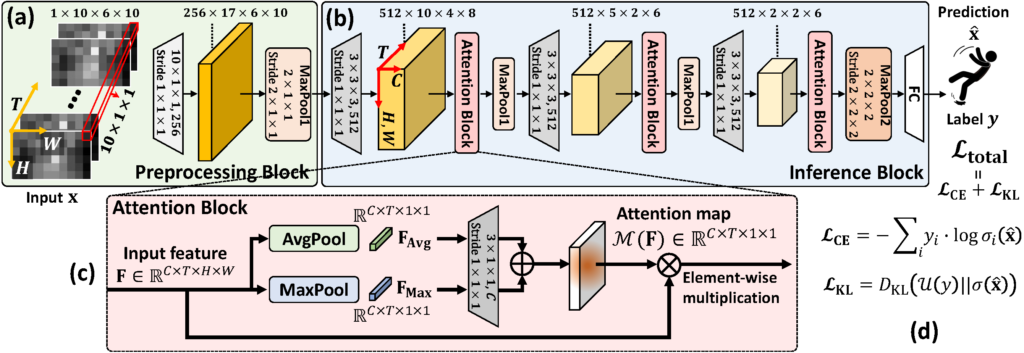
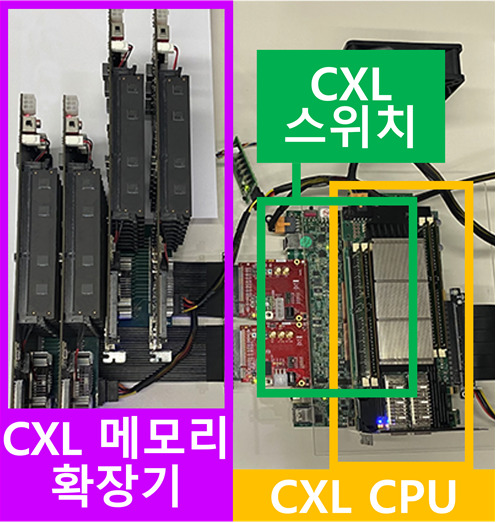
정명수 교수 연구팀(CAMEL)의 하이퍼스케일 AI를 위한 소프트웨어/하드웨어 설계 연구, 삼성미래기술육성사업 지원 선정

전기및전자공학부 CAMEL 연구팀(정명수 교수 연구실)이 “하이퍼스케일 AI를 위한 알고리즘 및 소프트웨어-하드웨어 프레임워크 공동 설계”라는 주제로 삼성미래기술육성사업에 선정되었다.
본 연구팀은 최근 크게 주목받고 있는 멀티모달(Multi-modal), 자동화 인코더(Auto-encorder), 다중전문가(Mixture of Expert)등을 사용하는 하이퍼스케일 AI 모델들의 연산 특징이 학습 과정 중 계속해서 변화함을 새롭게 발견하였으며, 이러한 발견을 기반으로 하이퍼스케일 AI 모델용 특화 알고리즘과 가속 소프트웨어 기술과 하드웨어 설계 등을 이번 과제를 통하여 새롭게 제시한다.
특히 기존 초거대 AI 가속 하드웨어/소프트웨어 기술이 초거대 파라미터와 입력 모델들을 처리하는 데 있어서 모델 레이어들 간, 다수 레이어들 내에서 수시로 계속 변화하는 데이터의 밀도와 연산의 특징들 추출하고 적절히 대응하지 못하여 생기는 문제들을 처음 발견하여 이를 정형화하였다.
정형화된 문제를 해결하기 위해서 CAMEL 연구팀은 실시간으로 하이퍼스케일 AI의 연산 특징들을 감지하고 변화한 연산 특징에 적합한 연산을 지원하는 동적 가속 기술을 제안한다.
이외에도 동적 가속을 위한 AI 반도체 하드웨어 설계, 관련 오픈소스 프레임워크등의 연구를 통해, 하이퍼스케일 AI 모델의 어려움을 해결하는 것을 넘어 현재 빠르게 성장 중인 딥러닝 서비스 분야 전반에 이득을 가져올 것으로 예상하고 있다.
삼성전자는 미래를 책임지는 과학기술 육성을 목표로 지난 2013년부터 1조 5천억원을 출연해 ‘미래기술육성사업’을 시행하고 있다.
이번에 선정된 자유공모 지원과제는 삼성미래기술육성사업의 10주년을 중심으로 기초과학, 소재, ICT 분야에서 새롭고 혁신적인 미래 기술 분야를 중점 지원의 기조에 맞춰 선정되었다.
CAMEL 연구팀은 이번 단독 과제 선정 전, 지난 2021년에도 그래프 신경망 기계학습 (GNN)을 위한 메모리 및 가속시스템을 주제로 삼성미래기술육성사업의 책임 연구팀으로 소프트웨어와 하드웨어스택 전체를 아우르는 다년간 과제를 수행한 경험이 있다.