Shinhwan Kang, Kyuhan Lee, and Kijung Shin
ICDE 2022: IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering 2022
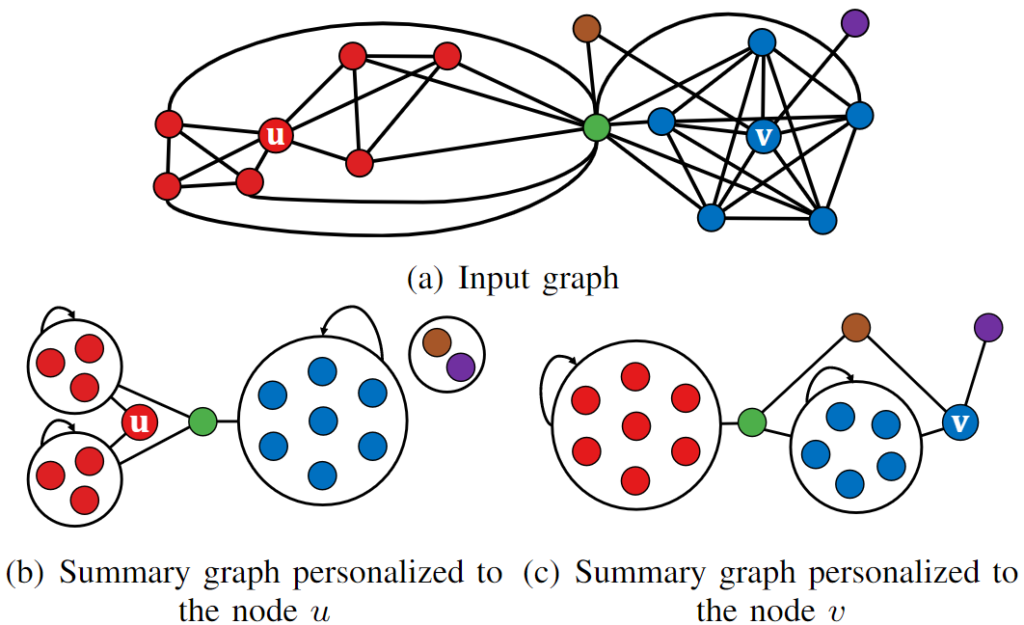
Abstract: Are users of an online social network interested equally in all connections in the network? If not, how can we obtain a summary of the network personalized to specific users? Can we use the summary for approximate query answering? As massive graphs (e.g., online social networks, hyperlink networks, and road networks) have become pervasive, graph compression has gained importance for the efficient processing of such graphs with limited resources. Graph summarization is an extensively-studied lossy compression method. It provides a summary graph where nodes with similar connectivity are merged into supernodes, and a variety of graph queries can be answered approximately from the summary graph. In this work, we introduce a new problem, namely personalized graph summarization, where the objective is to obtain a summary graph where more emphasis is put on connections closer to a given set of target nodes. Then, we propose PeGaSus, a linear-time algorithm for the problem. Through experiments on six real-world graphs, we demonstrate that PeGaSus is (a) Effective: node-similarity queries for target nodes can be answered significantly more accurately from personalized summary graphs than from non-personalized ones of similar size, (b) Scalable: it summarizes graphs with up to one billion edges, and (c) Applicable to distributed multi-query answering: it successfully replaces graph partitioning for communication-free multi-query processing.
Shinhwan Kang, Kyuhan Lee, and Kijung Shin
PAKDD 2022: Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining 2022
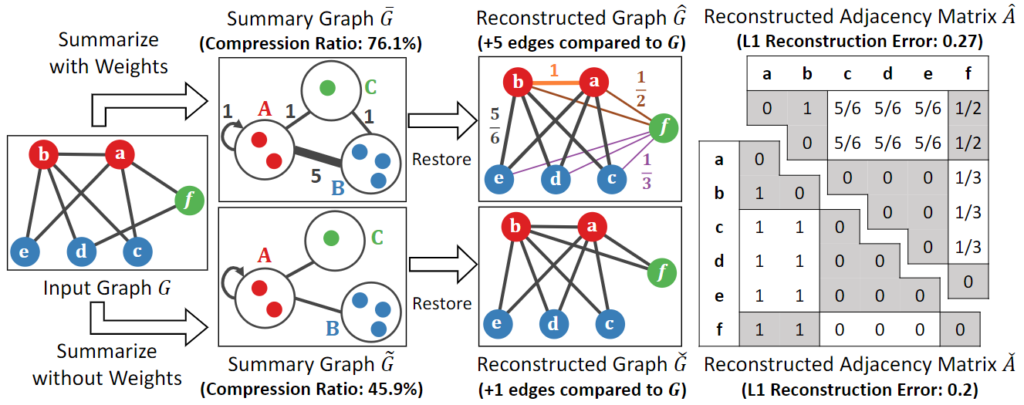
Abstract: Which one is better between two representative graph summarization models with and without edge weights? From web graphs to online social networks, large graphs are everywhere. Graph summarization, which is an effective graph compression technique, aims to find a compact summary graph that accurately represents a given large graph. Two versions of the problem, where one allows edge weights in summary graphs and the other does not, have been studied in parallel without direct comparison between their underlying representation models. In this work, we conduct a systematic comparison by extending three search algorithms to both models and evaluating their outputs on eight datasets in five aspects: (a) reconstruction error, (b) error in node importance, (c) error in node proximity, (d) the size of reconstructed graphs, and (e) compression ratios. Surprisingly, using unweighted summary graphs leads to outputs significantly better in all the aspects than using weighted ones, and this finding is supported theoretically. Notably, we show that a state-of-the-art algorithm can be improved substantially (specifically, 8.2X, 7.8X, and 5.9X in terms of (a), (b), and (c), respectively, when (e) is fixed) based on the observation.
Hyunjin Hwang*, Seungwoo Lee*, Chanyoung Park, and Kijung Shin
SIGIR 2022: International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval 2022
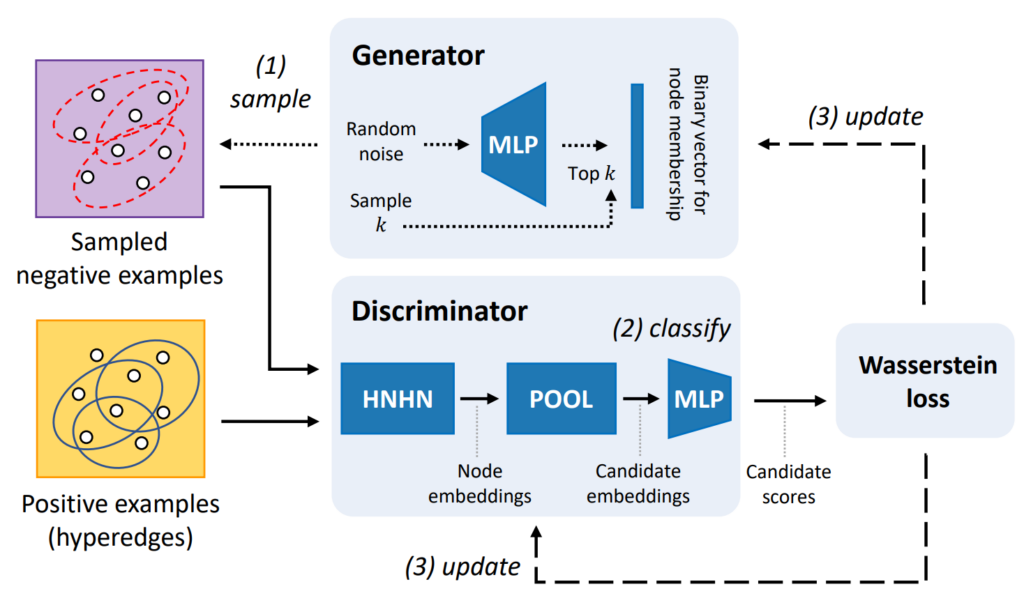
Abstract: Hypergraphs (i.e., sets of hyperedges) naturally represent group relations (e.g., researchers co-authoring a paper and ingredients used together in a recipe), each of which corresponds to a hyperedge (i.e., a subset of nodes). Predicting future or missing hyperedges bears significant implications for many applications (e.g., collaboration and recipe recommendation). What makes hyperedge prediction particularly challenging is the vast number of non-hyperedge subsets, which grows exponentially with the number of nodes. Since it is prohibitive to use all of them as negative examples for model training, it is inevitable to sample a very small portion of them, and to this end, heuristic sampling schemes have been employed. However, trained models suffer from poor generalization capability for examples of different natures. In this paper, we propose AHP, an adversarial training-based hyperedge-prediction method. It learns to sample negative examples without relying on any heuristic schemes. Using six real hypergraphs, we show that AHP generalizes better to negative examples of various natures. It yields up to 28.2% higher AUROC than the best existing methods and often even outperforms its variants with sampling schemes tailored to test sets.
Geon Lee, Minyoung Choe and Kijung Shin
IJCAI 2022: International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence 2022
Abstract: Sequences of group interactions, such as emails, online discussions, and co-authorships, are ubiquitous; and they are naturally represented as a stream of hyperedges. Despite their broad potential applications, anomaly detection in hypergraphs (i.e., sets of hyperedges) has received surprisingly little attention, compared to that in graphs. While it is tempting to reduce hypergraphs to graphs and apply existing graph-based methods, according to our experiments, taking higher-order structures of hypergraphs into consideration is worthwhile. We propose HashNWalk, an incremental algorithm that detects anomalies in a stream of hyperedges. It maintains and updates a constant-size summary of the structural and temporal information about the stream. Using the summary, which is the form of a proximity matrix, HashNWalk measures the anomalousness of each new hyperedge as it appears. HashNWalk is (a) Fast: it processes each hyperedge in near real-time and billions of hyperedges within a few hours, (b) Space Efficient: the size of the maintained summary is a predefined constant, (c) Effective: it successfully detects anomalous hyperedges in real-world hypergraphs.
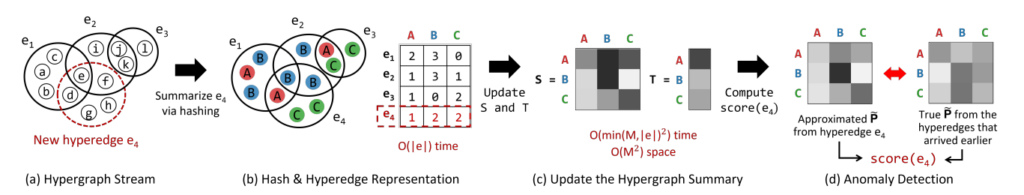
Geon Lee, Se-eun Yoon, and Kijung Shin
PLOS ONE
Abstract: Given a sequence of epidemic events, can a single epidemic model capture its dynamics during the entire period? How should we divide the sequence into segments to better capture the dynamics? Throughout human history, infectious diseases (e.g., the Black Death and COVID-19) have been serious threats. Consequently, understanding and forecasting the evolving patterns of epidemic events are critical for prevention and decision making. To this end, epidemic models based on ordinary differential equations (ODEs), which effectively describe dynamic systems in many fields, have been employed. However, a single epidemic model is not enough to capture long-term dynamics of epidemic events especially when the dynamics heavily depend on external factors (e.g., lockdown and the capability to perform tests). In this work, we demonstrate that properly dividing the event sequence regarding COVID-19 (specifically, the numbers of active cases, recoveries, and deaths) into multiple segments and fitting a simple epidemic model to each segment leads to a better fit with fewer parameters than fitting a complex model to the entire sequence. Moreover, we propose a methodology for balancing the number of segments and the complexity of epidemic models, based on the Minimum Description Length principle. Our methodology is (a) Automatic: not requiring any user-defined parameters, (b) Model-agnostic: applicable to any ODE-based epidemic models, and (c) Effective: effectively describing and forecasting the spread of COVID-19 in 70 countries.

Jihoon Ko*, Kyuhan Lee*, Hyunjin Hwang*, Seok-Geun Oh, Seok-Woo Son, and Kijung Shin
Computers and Geosciences
Abstract: Deep learning has been successfully applied to precipitation nowcasting. In this work, we propose a pre-training scheme and a new loss function for improving deep-learning-based nowcasting. First, we adapt U-Net, a widely- used deep-learning model, for the two problems of interest here: precipitation nowcasting and precipitation estimation from radar images. We formulate the former as a classification problem with three precipitation intervals and the latter as a regression problem. For these tasks, we propose to pre-train the model to predict radar images in the near future without requiring ground-truth precipitation, and we also propose the use of a new loss function for fine-tuning to mitigate the class imbalance problem. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach using radar images and precipitation datasets collected from South Korea over seven years. It is highlighted that our pre-training scheme and new loss function improve the critical success index (CSI) of nowcasting of heavy rainfall (at least 10 mm/hr) by up to 95.7% and 43.6%, respectively, at a 5-hr lead time. We also demonstrate that our approach reduces the precipitation estimation error by up to 10.7%, compared to the conventional approach, for light rainfall (between 1 and 10 mm/hr). Lastly, we report the sensitivity of our approach to different resolutions and a detailed analysis of four cases of heavy rainfall
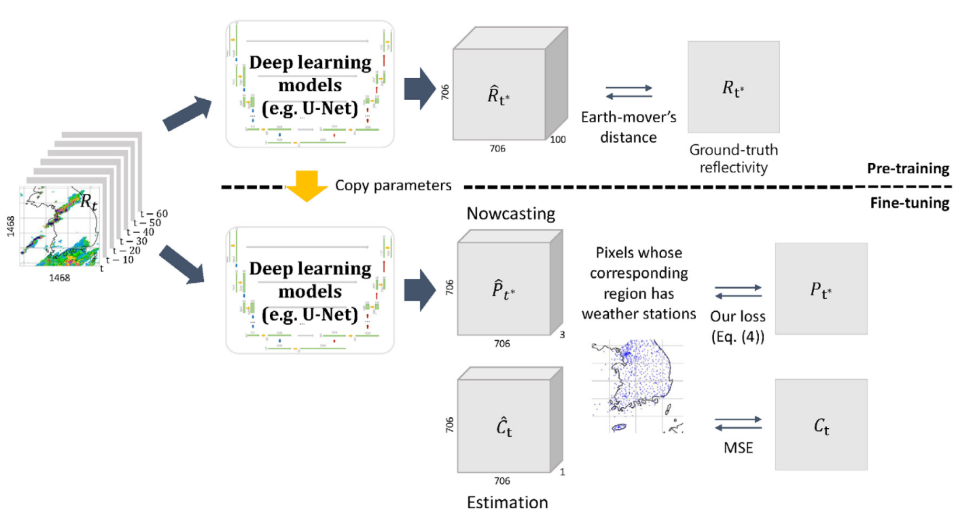
Jihoon Ko*, Yunbum Kook*, and Kijung Shin
Knowledge and Information Systems
Abstract: What kind of macroscopic structural and dynamical patterns can we observe in real-world hypergraphs? What can be underlying local dynamics on individuals, which ultimately lead to the observed patterns, beyond apparently random evolution? Graphs, which provide effective ways to represent pairwise interactions among entities, fail to represent group interactions (e.g., collaborations of three or more researchers, etc.). Regarded as a generalization of graphs, hypergraphs allowing for various sizes of edges prove fruitful in addressing this limitation. However, the increased complexity makes it challenging to understand hypergraphs as thoroughly as graphs. In this work, we closely examine seven structural and dynamical properties of real hypergraphs from six domains. To this end, we define new measures, extend notions of common graph properties to hypergraphs, and assess the significance of observed patterns by comparison with a null model and statistical tests. We also propose HYPERFF, a stochastic model for generating realistic hypergraphs. Its merits are three-fold: (a) Realistic: it successfully reproduces all seven patterns, in addition to five patterns established in previous studies, (b) Self-contained: unlike previously proposed models, it does not rely on oracles (i.e., unexplainable external information) at all, and it is parameterized by just two scalars, and (c) Emergent: it relies on simple and interpretable mechanisms on individual entities, which do not trivially enforce but surprisingly lead to macroscopic properties. While HYPERFF is mathematically intractable, we provide theoretical justifications and mathematical analysis based on its simplified version.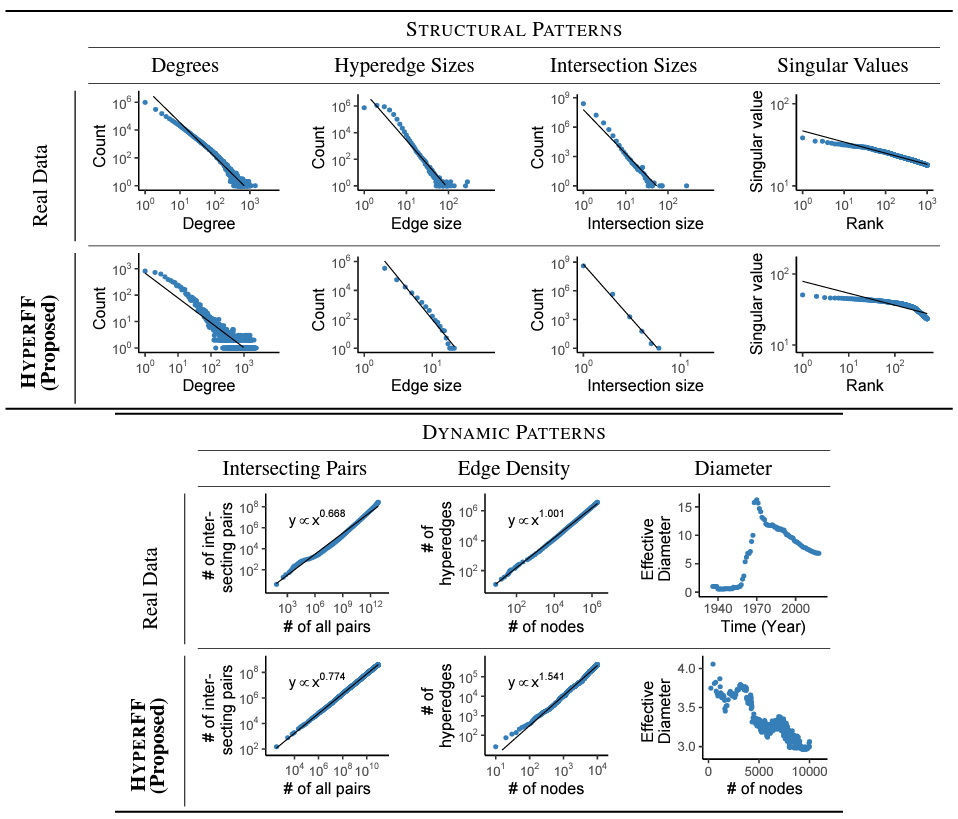
Manh Tuan Do, Noseong Park, Kijung Shin
Neural Processing Letters
Graph neural networks (GNNs) have received massive attention in the field of machine learning on graphs. Inspired by the success of neural networks, a line of research has been conducted to train GNNs to deal with various tasks, such as node classification, graph classification, and link prediction. In this work, our task of interest is graph classification. Several GNN models have been proposed and shown great accuracy in this task. However, the question is whether usual training methods fully realize the capacity of the GNN models. In this work, we propose a two-stage training framework based on triplet loss. In the first stage, GNN is trained to map each graph to a Euclidean-space vector so that graphs of the same class are close while those of different classes are mapped far apart. Once graphs are well-separated based on labels, a classifier is trained to distinguish between different classes. This method is generic in the sense that it is compatible with any GNN model. By adapting five GNN models to our method, we demonstrate the consistent improvement in accuracy and utilization of each GNN’s allocated capacity over the original training method of each model up to 5.4% points in 12 datasets.
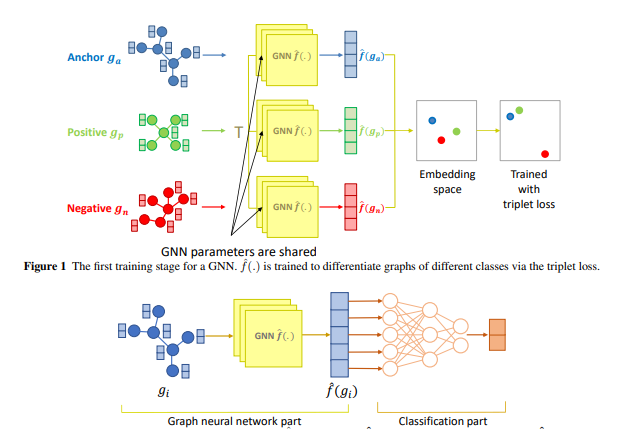
Geon Lee, Chanyoung Park, and Kijung Shin
ICDM 2022: IEEE International Conference on Data Mining
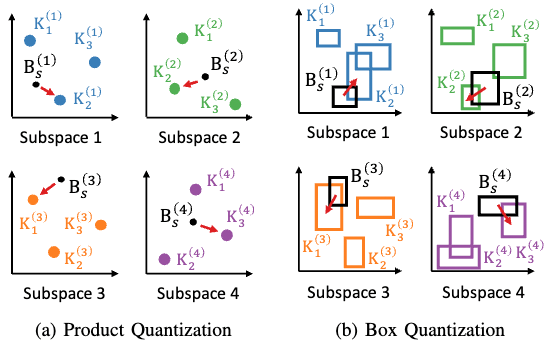
Abstract: Sets have been used for modeling various types of objects (e.g., a document as the set of keywords in it and a customer as the set of the items that she has purchased). Measuring similarity (e.g., Jaccard Index) between sets has been a key building block of a wide range of applications, including, plagiarism detection, recommendation, and graph compression. However, as sets have grown in numbers and sizes, the computational cost and storage required for set similarity computation have become substantial, and this has led to the development of hashing and sketching based solutions. In this work, we propose Set2Box, a learning-based approach for compressed representations of sets from which various similarity measures can be estimated accurately in constant time. The key idea is to represent sets as boxes to precisely capture overlaps of sets. Additionally, based on the proposed box quantization scheme, we design Set2Box+, which yields more concise but more accurate box representations of sets. Through extensive experiments on 8 real-world datasets, we show that, compared to baseline approaches, Set2Box+ is (a) Accurate: achieving up to 40.8X smaller estimation error while requiring 60% fewer bits to encode sets, (b) Concise: yielding up to 96.8X more concise representations with similar estimation error, and (c) Versatile: enabling the estimation of four set-similarity measures from a single representation of each set.
Sunwoo Kim, Minyoung Choe, Jaemin Yoo, and Kijung Shin
ICDM 2022: IEEE International Conference on Data Mining
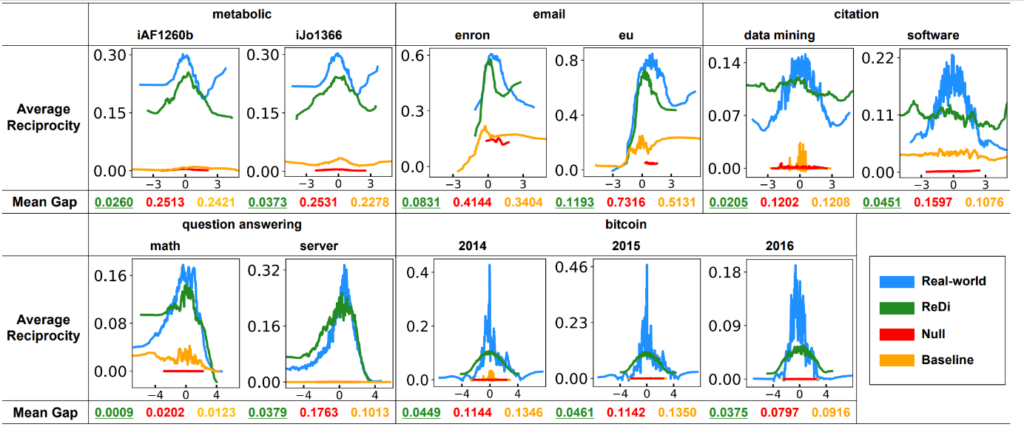
Abstract: Group interactions are prevalent in a variety of areas. Many of them, including email exchanges, chemical reactions, and bitcoin transactions, are directional, and thus they are naturally modeled as directed hypergraphs, where each hyperarc consists of the set of source nodes and the set of destination nodes. For directed graphs, which are a special case of directed hypergraphs, reciprocity has played a key role as a fundamental graph statistic in revealing organizing principles of graphs and in solving graph learning tasks. For general directed hypergraphs, however, even no systematic measure of reciprocity has been developed. In this work, we investigate the reciprocity of 11 real-world hypergraphs. To this end, we first introduce eight axioms that any reasonable measure of reciprocity should satisfy. Second, we propose HyperRec, a principled measure of hypergraph reciprocity that satisfies all the axioms. Third, we develop Ferret, a fast and exact algorithm for computing the measure, whose search space is up to smaller than that of naive computation. Fourth, using them, we examine 11 real-world hypergraphs and discover patterns that distinguish them from random hypergraphs. Lastly, we propose ReDi, an intuitive generative model for directed hypergraphs exhibiting the patterns.