육군 본부에서 주최하는 이번 대회는 건물 외부 주차장에서 출발하여 2층 창문으로 진입 후 여러 방들을 탐사하며 숨겨져 있는 특정 객체들을 찾아내고 그 종류와 위치를 관제 센터로 실시간 전송, 홈으로 복귀 등의 임무가 주어졌다.
심현철교수 연구팀의 실내 자율 비행 기술 연구는 미래 전장상황, 재난 상황에서 사용될 실내 정찰 드론의 핵심기술로 이번 대회를 통해 KAIST의 자율 비행 드론 기술 역량을 다시한번 알리는 계기가 되었다.


육군 본부에서 주최하는 이번 대회는 건물 외부 주차장에서 출발하여 2층 창문으로 진입 후 여러 방들을 탐사하며 숨겨져 있는 특정 객체들을 찾아내고 그 종류와 위치를 관제 센터로 실시간 전송, 홈으로 복귀 등의 임무가 주어졌다.
심현철교수 연구팀의 실내 자율 비행 기술 연구는 미래 전장상황, 재난 상황에서 사용될 실내 정찰 드론의 핵심기술로 이번 대회를 통해 KAIST의 자율 비행 드론 기술 역량을 다시한번 알리는 계기가 되었다.


KAIST 유민수 교수팀, 세계 최초 개인정보 보호 적용된 인공지능 반도체 개발,
구글 TPUv3 대비 차등 프라이버시 학습 과정을 3.6배 빠르게


전기및전자공학부 황의종 교수님과 전산학부 이재길 교수님 연구팀에서 신뢰할 수 있는 인공지능의 주요 요소인 공정성과 견고성에 대한 튜토리얼을 진행했습니다. 본 튜토리얼에는 노유지 박사과정(지도교수 황의종)과 송환준 박사(네이버 AI, KAIST 이재길 교수님 연구실 졸업)가 참여했습니다.
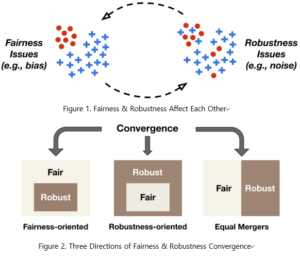
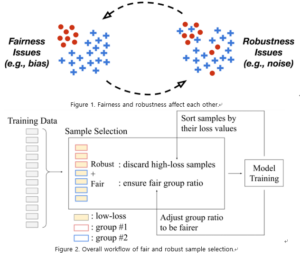
최근 머신러닝 기술의 화려한 성과 이면에 다양한 신뢰성 문제가 존재함이 지속적으로 드러나고 있습니다. 이에 따라 단순히 높은 정확도를 가지는 것을 넘어서, 공정성(fairness), 견고성(robustness), 투명성(transparency), 설명가능성(explainability) 등의 요소를 갖춘 인공지능의 필요성이 대두되고 있습니다.
본 튜토리얼에서는 신뢰할 수 있는 인공지능을 위한 필수 요소 중, 학습 데이터 내에서 서로 상호 영향을 미치는 공정성(fairness)과 견고성(robustness)을 함께 다루었습니다. 연구팀은 먼저 공정성과 견고성이라는 두 개의 축을 각각 구성하는 핵심 연구들을 소개하고, 더 나아가 최근 활발히 연구되기 시작한 두 요소의 “융합(convergence)”에 대한 주요 관점들을 정립했습니다.
본 연구팀은 해당 튜토리얼을 통해 공정하고 견고한 인공지능을 위한 연구의 방향성을 제시할 수 있을 것이라고 설명했습니다. 또한 인공지능의 신뢰성 문제에 대한 중요도가 더욱 높아짐에 따라, 해당 튜토리얼이 갖는 시의성이 매우 클 것으로 예상됩니다. 본 튜토리얼은 데이터마이닝 최고 권위 학회인 ACM SIGKDD (Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining) 2021에서 발표되었습니다.
자세한 튜토리얼 내용은 하단의 링크에서 확인하실 수 있습니다.
[Tutorial Information and Links
Title: Machine Learning Robustness, Fairness, and their Convergence (Tutorial)
Authors: Jae-Gil Lee (KAIST CS), Yuji Roh (KAIST EE), Hwanjun Song (Naver AI Lab), Steven Euijong Whang (KAIST EE)
논문 링크: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3447548.3470799?sid=SCITRUS
튜토리얼 자료: https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/1mV6oF_boGtnk14qh64Y4DaiKstcGJIfZiw-5AgTTgVQ/edit?usp=sharing
튜토리얼 영상: https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PLHULDvHaIwSwnbwkAOrJSs_TMQl1nhZ72
튜토리얼 홈페이지: https://kdd21tutorial-robust-fair-learning.github.io/
전기및전자공학부 황의종 교수님과 서창호 교수님 연구팀에서 공정하고 견고한 머신러닝 모델 학습을 위한 새로운 데이터 샘플 선택 기법을 개발했습니다. 본 연구는 노유지 박사과정(지도교수 황의종)이 주저자로 참여했고, 위스콘신 매디슨 전기컴퓨터공학부 이강욱 교수님과의 공동 연구로 진행되었습니다.
인공지능 기술이 사회 전반에 걸쳐 광범위하게 활용되면서, 인공지능의 신뢰성 문제가 점차 대두되고 있습니다. 이에 따라 단순히 높은 정확도를 가지는 것을 넘어서, 공정성(fairness), 견고성(robustness), 설명가능성(explainability) 등의 요소를 갖춘 인공지능의 필요성에 대한 사회적인 공감이 커지고 있습니다.
본 연구팀은 신뢰할 수 있는 인공지능을 위한 필수 요소 중, 학습 데이터 내에서 서로 상호 영향을 미치는 공정성(fairness)과 견고성(robustness)을 함께 높일 수 있는 새로운 데이터 샘플 선택 기법을 제안합니다. 기존의 공정성과 견고성을 위한 머신러닝 기법들은 알고리즘 자체에 큰 수정이 필요하거나 추가적인 외부 데이터의 활용이 요구되었는데, 이와는 달리 본 샘플 선택 기법은 데이터를 샘플링하는 배치 선택 단계에서 한 줄의 코드 변경만으로 공정성과 견고성을 효과적으로 달성합니다. 본 기법은 세 개의 최적화 문제의 결합을 기반으로 하며, 학습 데이터가 손상되었을 때에도 공정성과 견고성을 동시에 높일 수 있음을 보였습니다.
연구팀은 본 샘플 선택 기법이 높은 성능을 달성함과 동시에 실제 머신러닝 파이프라인에 쉽게 적용될 수 있다는 장점을 가졌기에, 해당 학습 기법을 다양한 어플리케이션에 적용할 수 있을 것이라고 설명했습니다. 또한 신뢰할 수 있는 인공지능에 대한 사회적 요구가 더욱 커짐에 따라, 이에 대한 활발한 후속 연구가 진행될 것으로 예상됩니다. 본 연구 성과는 머신러닝 최고 권위 학회인 NeurIPS (Neural Information Processing Systems) 2021에서 발표되었습니다.
자세한 연구 내용은 하단의 링크에서 확인하실 수 있습니다.
[Paper information and links]
Title: Sample Selection for Fair and Robust Training
Authors: Yuji Roh (KAIST EE), Kangwook Lee (Wisconsin-Madison Electrical & Computer Engineering), Steven Euijong Whang (KAIST EE), and Changho Suh (KAIST EE)
Paper: https://openreview.net/forum?id=2Dg2UQyRpQ
Source code: https://github.com/yuji-roh/fair-robust-selection
Slides: https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/1lauJc5lQEG4UEivts8OiosuI78KSLR6PJL1r47_aaus/edit?usp=sharing
Motivation
The growing use of next-generation sequencing and enlarged sequencing throughput require efficient short-read alignment, where seeding is one of the major performance bottlenecks. The key challenge in the seeding phase is searching for exact matches of substrings of short reads in the reference DNA sequence. Existing algorithms, however, present limitations in performance due to their frequent memory accesses.
Results
This article presents BWA-MEME, the first full-fledged short read alignment software that leverages learned indices for solving the exact match search problem for efficient seeding. BWA-MEME is a practical and efficient seeding algorithm based on a suffix array search algorithm that solves the challenges in utilizing learned indices for SMEM search which is extensively used in the seeding phase. Our evaluation shows that BWA-MEME achieves up to 3.45× speedup in seeding throughput over BWA-MEM2 by reducing the number of instructions by 4.60×, memory accesses by 8.77× and LLC misses by 2.21×, while ensuring the identical SAM output to BWA-MEM2.

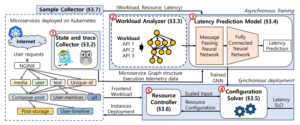
Microservice is an architectural style that has been widely adopted in various latency-sensitive applications. Similar to the monolith, autoscaling has attracted the attention of operators for managing resource utilization of microservices. However, it is still challenging to optimize resources in terms of latency service-level-objective (SLO) without human intervention. In this paper, we present GRAF, a graph neural network-based proactive resource allocation framework for minimizing total CPU resources while satisfying latency SLO. GRAF leverages front-end workload, distributed tracing data, and machine learning approaches to (a) observe/estimate impact of traffic change (b) find optimal resource combinations (c) make proactive resource allocation. Experiments using various open-source benchmarks demonstrate that GRAF successfully targets latency SLO while saving up to 19% of total CPU resources compared to the fine-tuned autoscaler. Moreover, GRAF handles traffic surge with 36% fewer resources while achieving up to 2.6x faster tail latency convergence compared to the Kubernetes autoscaler.
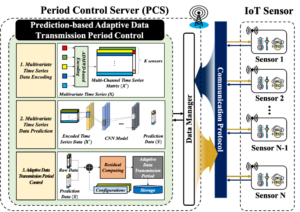
In order to reduce unnecessary data transmissions from Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, this paper proposes a multivariate time series prediction-based adaptive data transmission period control (PBATPC) algorithm for IoT networks. Based on the spatio-temporal correlation between multivariate time series data, we developed a novel multivariate time series data encoding scheme utilizing the proposed time series distance measure ADMWD
Composed of two significant factors for a multivariate time series prediction, i.e., the absolute deviation from the mean (ADM) and the weighted differential distance (WD), the ADMWD considers both the time distance from a prediction point and a negative correlation between the time series data concurrently.
Utilizing the convolutional neural network (CNN) model, a subset of IoT sensor readings can be predicted from encoded multivariate time series measurements, and we compared the predicted sensor values with actual readings to obtain the adaptive data transmission period. Extensive performance evaluations show a substantial performance gain of the proposed algorithm in terms of the average power reduction ratio (approximately 12%) and average data reconstruction error (approximately 8.32% MAPE). Finally, this paper also provides a practical implementation of the proposed PBATPC algorithm via the HTTP protocol under the IEEE 802.11-based WLAN network.
Authors: Seyeon Kim (KAIST), Kyungmin Bin (SNU), Sangtae Ha (CU Boulder), Song Chong (KAIST)
Abstract:
DVFS(dynamic voltage and frequency scaling) is a system-level technique that adjusts voltage and frequency levels of CPU/GPU at runtime to balance energy efficiency and high performance. DVFS has been studied for many years, but it is considered still challenging to realize a DVFS that performs ideally for mobile devices for two main reasons: i) an optimal power budget distribution between CPU and GPU in a power-constrained platform can only be defined by the application performance, but conventional DVFS implementations are mostly application-agnostic; ii) mobile platforms experience dynamic thermal environments for many reasons such as mobility and holding methods, but conventional implementations are not adaptive enough to such environmental changes. In this work, we propose a deep reinforcement learning-based frequency scaling technique, zTT. zTT learns thermal environmental characteristics and jointly scales CPU and GPU frequencies to maximize the application performance in an energy-efficient manner while achieving zero thermal throttling. Our evaluations for zTT implemented on Google Pixel 3a and NVIDIA JETSON TX2 platform with various applications show that zTT can adapt quickly to changing thermal environments, consistently resulting in high application performance with energy efficiency. In a high-temperature environment where a rendering application with the default mobile DVFS fails to keep producing more than a target frame rate, zTT successfully manages to do so even with 23.9% less average power consumption.
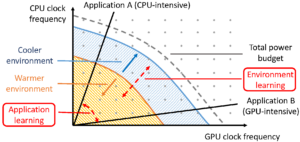
<The purpose and impact of learning in zTT>
(Figure) Figure illustrates the purpose and impact of learning in zTT. The lattice points within the total power budget curve for a mobile device represent all available CPU/GPU power consumption combinations. The graph shows that the better the cooling, the more combinations are usable, thus providing better performance for an application. To find out the best possible combination at the moment, zTT learns the environment and application performance.
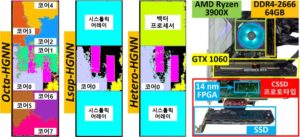
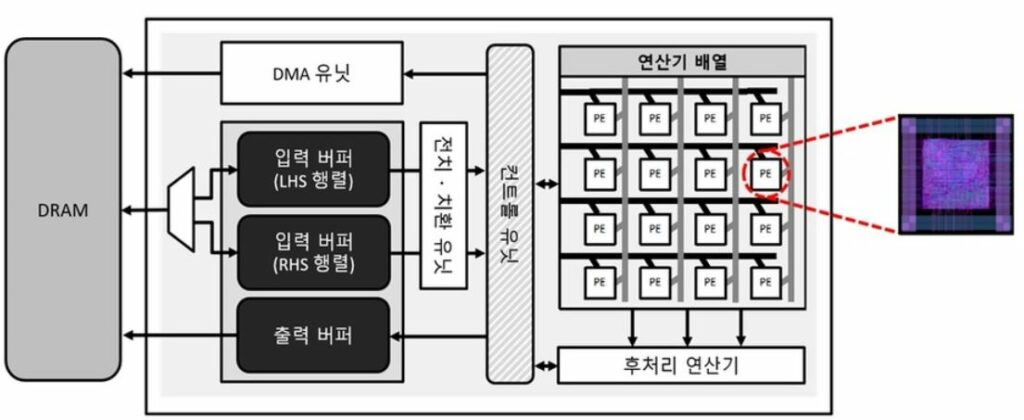
Graph neural networks (GNNs) process large-scale graphs consisting of a hundred billion edges. In contrast to traditional deep learning, unique behaviors of the emerging GNNs are engaged with a large set of graphs and embedding data on storage, which exhibits complex and irregular preprocessing. We propose a novel deep learning framework on large graphs, HolisticGNN, that provides an easy-to-use, nearstorage inference infrastructure for fast, energy-efficient GNN processing. To achieve the best end-to-end latency and high energy efficiency, HolisticGNN allows users to implement various GNN algorithms and directly executes them where the actual data exist in a holistic manner. It also enables RPC over PCIe such that the users can simply program GNNs through a graph semantic library without any knowledge of the underlying hardware or storage configurations. We fabricate HolisticGNN’s hardware RTL and implement its software on an FPGA-based computational SSD (CSSD). Our empirical evaluations show that the inference time of HolisticGNN outperforms GNN inference services using high-performance modern GPUs by 7.1× while reducing energy consumption by 33.2×, on average.
학과뉴스링크: https://ee.kaist.ac.kr/en/press/22890/
학회링크: https://www.usenix.org/conference/fast22/presentation/kwon