Journal: Advanced Intelligent Systems
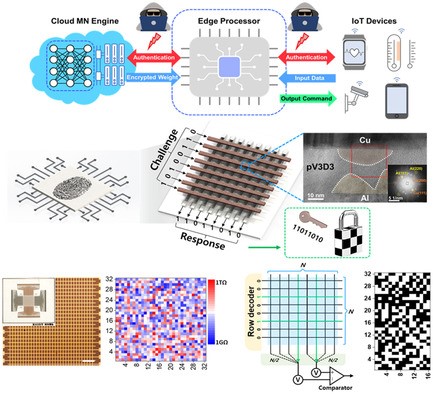
Abstract: Internet-of-things (IoT) edge devices with a memristive neuromorphic system can more effectively enhance daily lives. However, cyberattacks remain critical concerns for smart IoT edge devices that process a vast body of information via networks. Herein, a highly secure neuromorphic system is reported, which can be implemented using a physically unclonable function (PUF) that exploits the high entropy achieved via the stochastic switching of a poly(1,3,5-trivinyl-1,3,5-trimethyl cyclotrisiloxane) (pV3D3)-based memristor. The excellent insulating property of pV3D3 enhances the stochasticity of the tunneling distance for randomly ruptured Cu filaments. The pV3D3 memristor-based PUF (pV3D3-PUF) achieves near-ideal 50% averages for uniformity and uniqueness, excellent reliability under conditions of mechanical stress and water immersion, and reconfigurability-bolstering security without additional hardware. Using stochastic in-memory computing, the pV3D3-PUF shows resilience to machine learning attacks. Furthermore, a cryptography protocol is demonstrated, which enables artificial intelligence service implementation without security issues for PUF-integrated pV3D3 memristor-based neuromorphic systems.