Abstract


Recent advances in visual reinforcement learning (visual RL), which learns from high-dimensional image observations, have narrowed the gap between state-based and image-based training. However, visual RL continues to face significant challenges in robotic manipulation tasks involving occlusions, such as lifting obscured objects. Although high-resolution tactile sensors have shown promise in addressing these occlusion issues through visuotactile manipulation, their high cost and complexity limit widespread adoption. In this paper, we propose a novel RL approach that introduces multimodal fusion dualization and representation normalization to enhance sample efficiency and robustness in robotic manipulation tasks involving occlusions — without relying on tactile feedback. Our multimodal fusion dualization technique separates the fusion process into two distinct modules, each optimized individually for the actor and the critic, resulting in tailored representations for each network. Additionally, representation normalization techniques, including LayerNorm and SimplexNorm, are incorporated into the representation learning process to stabilize training and prevent issues such as gradient explosion. We demonstrate that our method not only effectively tackles challenging robotic manipulation tasks involving occlusions but also outperforms state-of-the-art visual RL and state-based RL methods in both sample efficiency and task performance. Notably, this is achieved without relying on tactile sensors or prior knowledge, such as predefined low-dimensional coordinate states or pre-trained representations, making our approach both cost-effective and scalable for real-world robotic applications.
Main Figure

Abstract
There is a growing concern about applying batch normalization (BN) in adversarial training (AT), especially when the model is trained on both adversarial samples and clean samples (termed Hybrid-AT). With the assumption that adversarial and clean samples are from two different domains, a common practice in prior works is to adopt Dual BN, where BN and BN are used for adversarial and clean branches, respectively. A popular belief for motivating Dual BN is that estimating normalization statistics of this mixture distribution is challenging and thus disentangling it for normalization achieves stronger robustness. In contrast to this belief, we reveal that disentangling statistics plays a less role than disentangling affine parameters in model training. This finding aligns with prior work (Rebuffi et al., 2023), and we build upon their research for further investigations. We demonstrate that the domain gap between adversarial and clean samples is not very large, which is counter-intuitive considering the significant influence of adversarial perturbation on the model accuracy. We further propose a two-task hypothesis which serves as the empirical foundation and a unified framework for Hybrid-AT improvement. We also investigate Dual BN in test-time and reveal that affine parameters characterize the robustness during inference. Overall, our work sheds new light on understanding the mechanism of Dual BN in Hybrid-AT and its underlying justification.
Main Figure

Abstract
Designing effective reward functions remains a fundamental challenge in reinforcement learning (RL), as it often requires extensive human effort and domain expertise. While RL from human feedback has been successful in aligning agents with human intent, acquiring high-quality feedback is costly and labor-intensive, limiting its scalability. Recent advancements in foundation models present a promising alternative–leveraging AI-generated feedback to reduce reliance on human supervision in reward learning. Building on this paradigm, we introduce ERL-VLM, an enhanced rating-based RL method that effectively learns reward functions from AI feedback. Unlike prior methods that rely on pairwise comparisons, ERL-VLM queries large vision-language models (VLMs) for absolute ratings of individual trajectories, enabling more expressive feedback and improved sample efficiency. Additionally, we propose key enhancements to rating-based RL, addressing instability issues caused by data imbalance and noisy labels. Through extensive experiments across both low-level and high-level control tasks, we demonstrate that ERL-VLM significantly outperforms existing VLM-based reward generation methods. Our results demonstrate the potential of AI feedback for scaling RL with minimal human intervention, paving the way for more autonomous and efficient reward learning.
Main Figure

Abstract
We consider the generative modeling of speech over multiple minutes, a requirement for longform multimedia generation and audio-native voice assistants. However, textless spoken language models struggle to generate plausible speech past tens of seconds, due to high temporal resolution of speech tokens causing loss of coherence, architectural issues with long-sequence training or extrapolation, and memory costs at inference time. From these considerations we derive SpeechSSM, the first speech language model family to learn from and sample long-form spoken audio (e.g., 16 minutes of read or extemporaneous speech) in a single decoding session without text intermediates. SpeechSSMs leverage recent advances in linear-time sequence modeling to greatly surpass current Transformer spoken LMs in coherence and efficiency on multi-minute generations while still matching them at the utterance level. As we found current spoken language evaluations uninformative, especially in this new longform setting, we also introduce: LibriSpeechLong, a benchmark for long-form speech evaluation; new embedding-based and LLM-judged metrics; and quality measurements over length and time. Speech samples, the LibriSpeech-Long dataset, and any future code or model releases can be found at https://google.github.io/tacotron/publications/speechssm/
Main Figure

We introduce ConfPO, a method for preference learning in Large Language Models (LLMs) that identifies and optimizes preference-critical tokens based solely on the training policy’s confidence, without requiring any auxiliary models or compute. Unlike prior Direct Alignment Algorithms (DAAs) such as Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), which uniformly adjust all token probabilities regardless of their relevance to preference, ConfPO focuses optimization on the most impactful tokens. This targeted approach improves alignment quality while mitigating overoptimization (i.e., reward hacking) by using the KL divergence budget more efficiently. In contrast to recent token-level methods that rely on credit-assignment models or AI annotators, raising concerns about scalability and reliability, ConfPO is simple, lightweight, and model-free. Experimental results on challenging alignment benchmarks, including AlpacaEval 2 and Arena-Hard, demonstrate that ConfPO consistently outperforms uniform DAAs across various LLMs, delivering better alignment with zero additional computational
overhead. The code is publicly accessible at https://github.com/hee-suk-yoon/ConfPO.
Main Figure

Abstract
Unlike fixed- or variable-rate image coding, progressive image coding (PIC) aims to compress various qualities of images into a single bitstream, increasing the versatility of bitstream utilization and providing high compression efficiency compared to simulcast compression. Research on neural network (NN)-based PIC is in its early stages, mainly focusing on applying varying quantization step sizes to the transformed latent representations in a hierarchical manner. These approaches are designed to compress only the progressively added information as the quality improves, considering that a wider quantization interval for lower-quality compression includes multiple narrower sub-intervals for higher-quality compression. However, the existing methods are based on handcrafted quantization hierarchies, resulting in sub-optimal compression efficiency. In this paper, we propose an NN-based progressive coding method that firstly utilizes learned quantization step sizes via learning for each quantization layer. We also incorporate selective compression with which only the essential representation components are compressed for each quantization layer. We demonstrate that our method achieves significantly higher coding efficiency than the existing approaches with decreased decoding time and reduced model size.
Main Figure

Title: That’s What I Said: Fully-Controllable Talking Face Generation
Authors: Y. Jang, K. Rho, J. Woo, H. Lee, J. Park, Y. Lim, B. Kim, J. S. Chung
Conference: ACM International Conference on Multimedia
Abstract: The goal of this paper is to synthesise talking faces with controllable facial motions. To achieve this goal, we propose two key ideas. The first is to establish a canonical space where every face has the same motion patterns but different identities. The second is to navigate a multimodal motion space that only represents motion-related features while eliminating identity information. To disentangle identity and motion, we introduce an orthogonality constraint between the two different latent spaces. From this, our method can generate natural-looking talking faces with fully controllable facial attributes and accurate lip synchronisation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art results in terms of both visual quality and lip-sync score. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to develop a talking face generation framework that can accurately manifest full target facial motions including lip, head pose, and eye movements in the generated video without any additional supervision beyond RGB video with audio.
Main Figure: 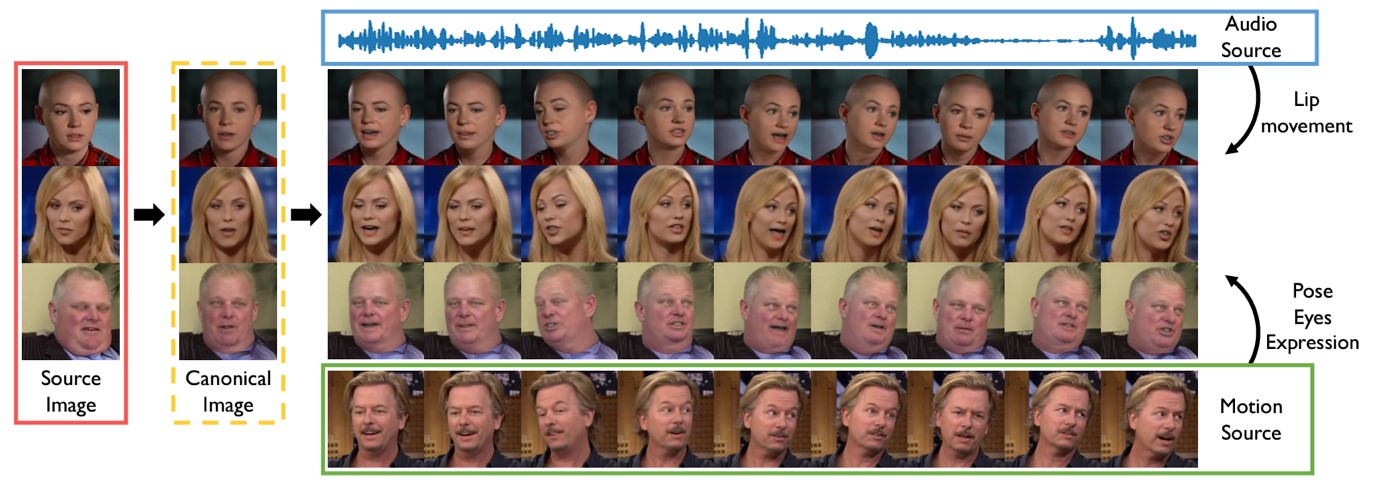
Title: Sound Source Localization is All about Cross-Modal Alignment
Authors: A. Senocak, H. Ryu, J. Kim, T. Oh, H. Pfister, J. S. Chung
Conference: International Conference on Computer Vision
Abstract: Humans can easily perceive the direction of sound sources in a visual scene, termed sound source localization. Recent studies on learning-based sound source localization have mainly explored the problem from a localization perspective. However, prior arts and existing benchmarks do not account for a more important aspect of the problem, cross-modal semantic understanding, which is essential for genuine sound source localization. Cross-modal semantic understanding is important in understanding semantically mismatched audio-visual events, e.g., silent objects, or offscreen sounds. To account for this, we propose a crossmodal alignment task as a joint task with sound source localization to better learn the interaction between audio and visual modalities. Thereby, we achieve high localization performance with strong cross-modal semantic understanding. Our method outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches in both sound source localization and cross-modal retrieval. Our work suggests that jointly tackling both tasks is necessary to conquer genuine sound source localization.
Main Figure:
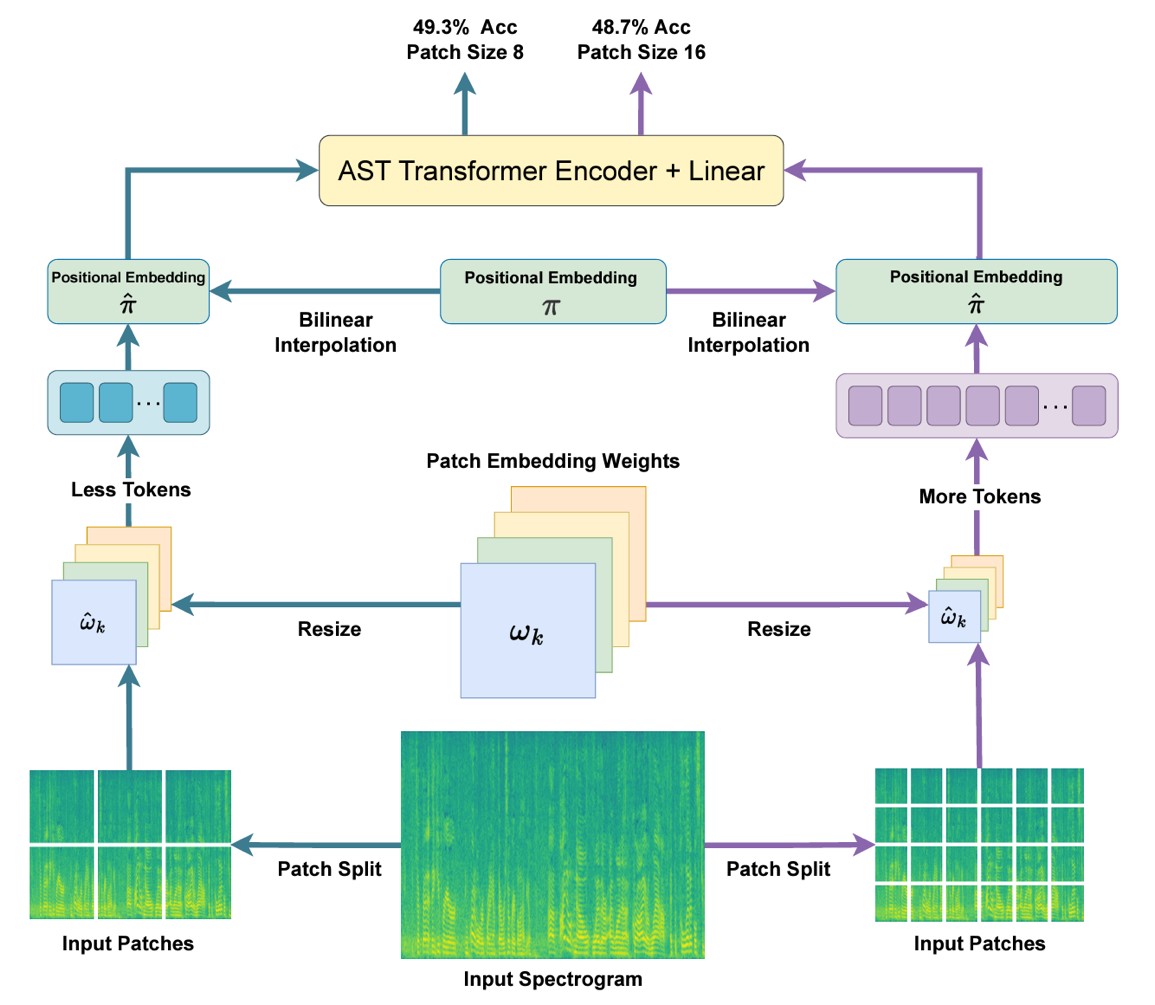
Title: FlexiAST: Flexibility is What AST Needs
Authors: J. Feng, M. H. Erol, J. S. Chung, A. Senocak
Conference: Interspeech
Abstract: The objective of this work is to give patch-size flexibility to Audio Spectrogram Transformers (AST). Recent advancements in ASTs have shown superior performance in various audio-based tasks. However, the performance of standard ASTs degrades drastically when evaluated using different patch sizes from that used during training. As a result, AST models are typically re-trained to accommodate changes in patch sizes. To overcome this limitation, this paper proposes a training procedure to provide flexibility to standard AST models without architectural changes, allowing them to work with various patch sizes at the inference stage- FlexiAST. This proposed training approach simply utilizes random patch size selection and resizing of patch and positional embedding weights. Our experiments show that FlexiAST gives similar performance to standard AST models while maintaining its evaluation ability at various patch sizes on different datasets for audio classification tasks.
Main Figure: