저자: 이상민, 김학구, 최대휘, 김형일, 노용만
초록: Our work addresses long-term motion context issues for predicting future frames. To predict the future precisely, it is required to capture which long-term motion context (e.g., walking or running) the input motion (e.g., leg movement) belongs to. The bottlenecks arising when dealing with the long-term motion context are: (i) how to predict the long-term motion context naturally matching input sequences with limited dynamics, (ii) how to predict the long-term motion context with high-dimensionality (e.g., complex motion). To address the issues, we propose novel motion context-aware video prediction. To solve the bottleneck (i), we introduce a long-term motion context memory (LMC-Memory) with memory alignment learning. The proposed memory alignment learning enables to store long-term motion contexts into the memory and to match them with sequences including limited dynamics. As a result, the long-term context can be recalled from the limited input sequence. In addition, to resolve the bottleneck (ii), we propose memory query decomposition to store local motion context (i.e., low-dimensional dynamics) and recall the suitable local context for each local part of the input individually. It enables to boost the alignment effects of the memory. Experimental results show that the proposed method outperforms other sophisticated RNN-based methods, especially in long-term condition. Further, we validate the effectiveness of the proposed network designs by conducting ablation studies and memory feature analysis. The source code of this work is available.
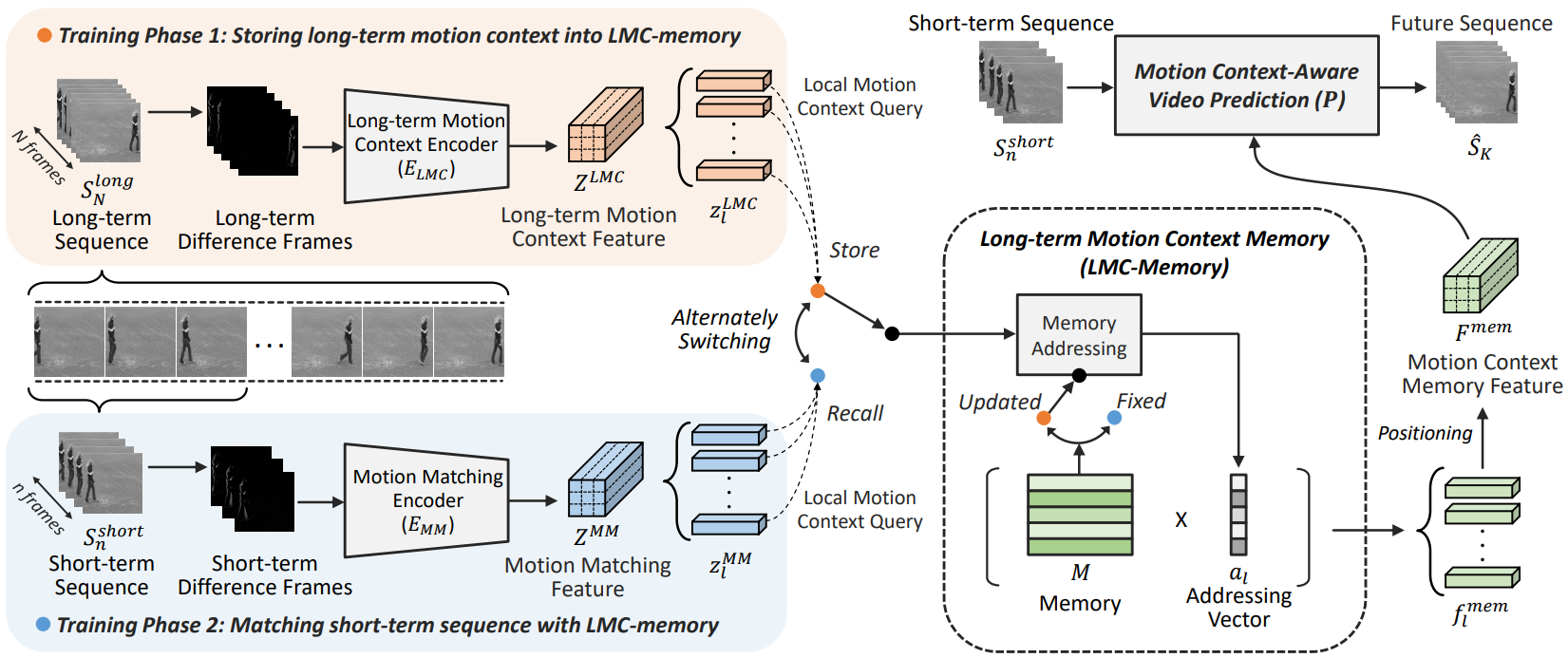
Figure 1. Memory alignment learning with long-term motion context memory
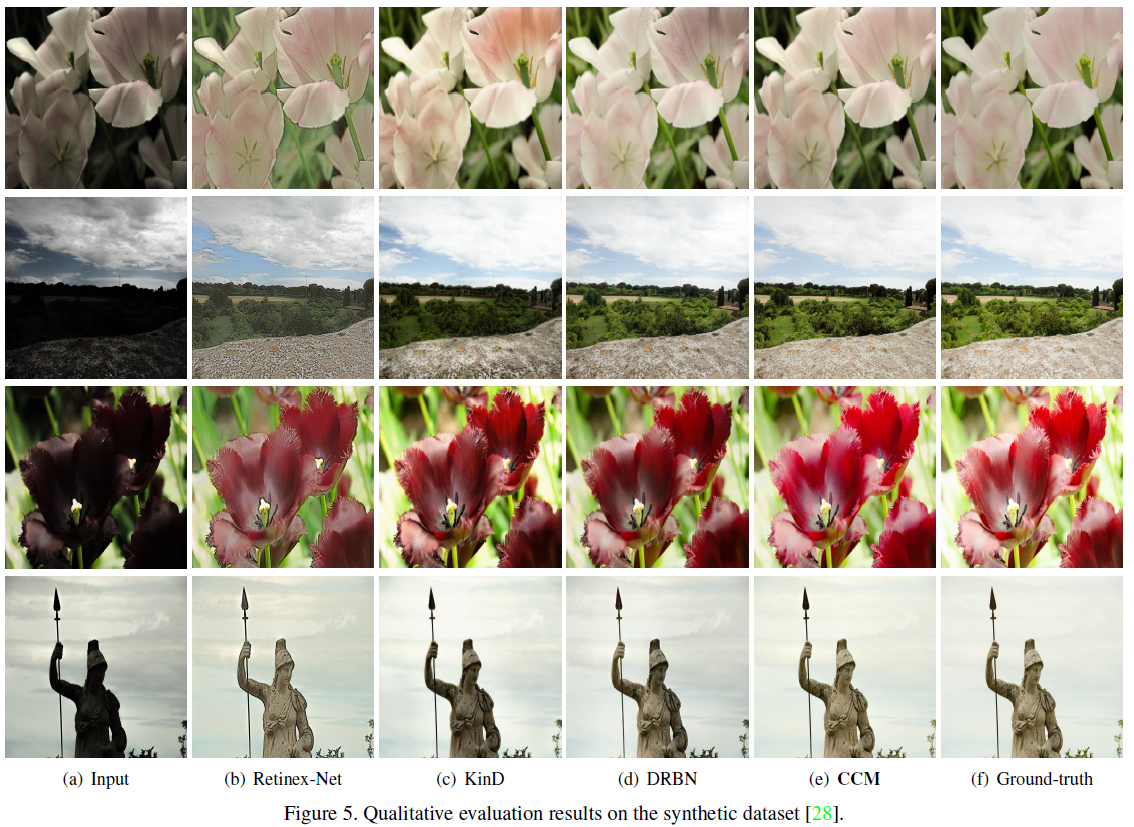
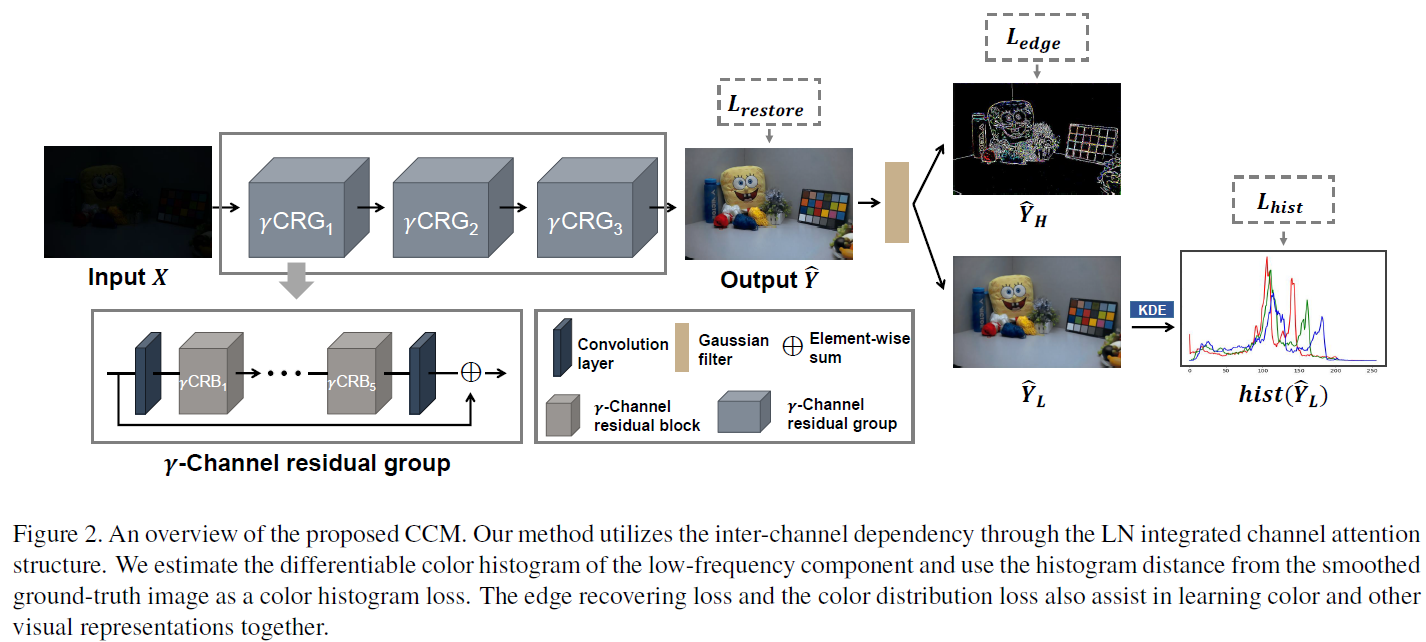
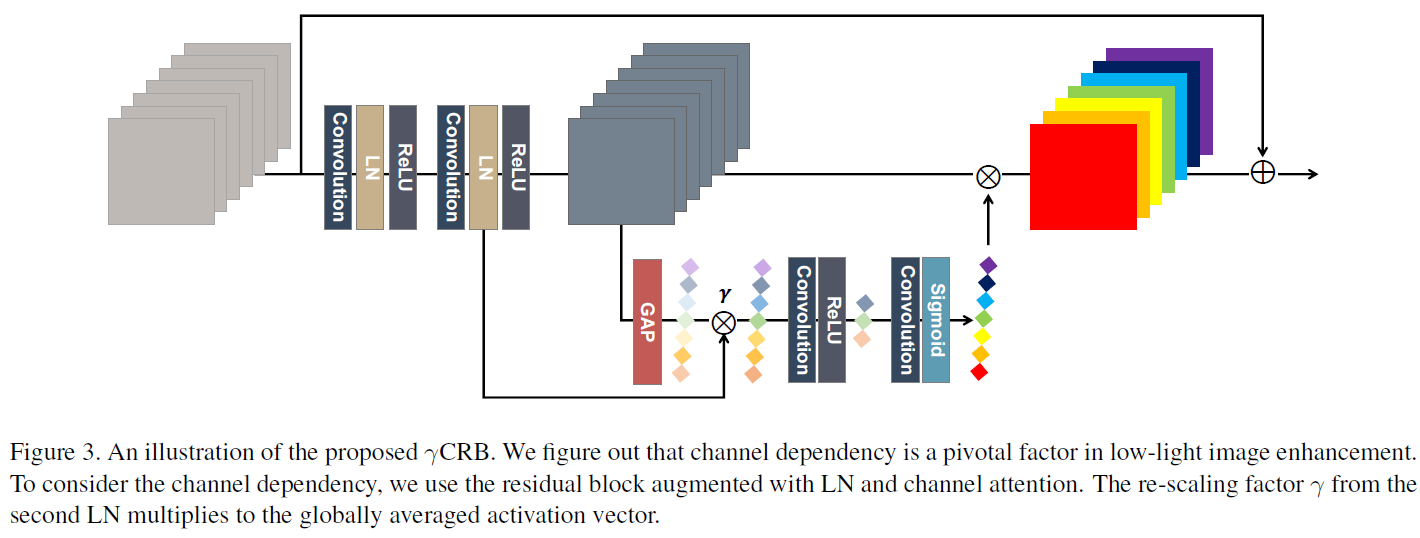
색상은 이미지에서 중요한 정보를 전달한다. 그러나 저조도 조건에서는 픽셀강도 뿐만 아니라 실제 색상 분포가 크게 바뀔 수 있다. 또한, 이러한 왜곡은 대부분 인버스 문제로 인해 복구할 수 없다. 최근 연구에서는 저조도 이미지 향상을 위한 학습 기반의 방법들이 발전해왔다. 하지만 대부분의 딥러닝 방법은 하이레벨의 객체 지향 정보를 복원하는 것을 복표로 한다. 본 논문에서는 학습 기반의 방법론이 색상 정보를 복원하는데도 사용할 수 있다고 가정한다. 이 질문을 해결하기 위해 저조도 이미지 향상을 위한 새로운 색상 표현 학습 방법을 제안한다. 본 연구에서는 채널인식 레지듀얼 네트워크와 미분가능한 히스토그램을 사용하여 색상 특징을 캡처한다. 합성 및 실제 데이터세트를 사용한 실험 결과는 제안된 학습 방식이 최첨단 성능을 달성함을 시사한다. 본 연구를 통해 채널 간 의존성과 색상 분포 매칭이 저조도 조건에서 색상 표현을 학습하는 데 중요한 요소라는 결론을 내린다.
Conference/Journal, Year: BMVC, 2021
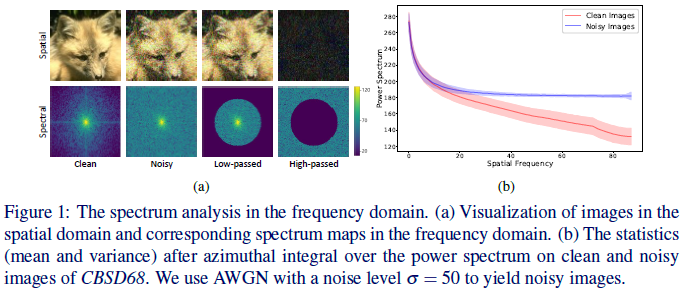
Supervised learning-based methods yield robust denoising results, yet they are inherently limited by the need for large-scale clean/noisy paired datasets. The use of unsupervised denoisers, on the other hand, necessitates a more detailed understanding of the underlying image statistics. In particular, it is well known that apparent differences between clean and noisy images are most prominent on high-frequency bands, justifying the use of low-pass filters as part of conventional image preprocessing steps. However, most learning-based denoising methods utilize only one-sided information from the spatial domain without considering frequency domain information. To address this limitation, in this study we propose a frequency-sensitive unsupervised denoising method. To this end, a generative adversarial network (GAN) is used as a base structure. Subsequently, we include spectral discriminator and frequency reconstruction loss to transfer frequency knowledge into the generator. Results using natural and synthetic datasets indicate that our unsupervised learning method augmented with frequency information achieves state-of- the-art denoising performance, suggesting that frequency domain information could be a viable factor in improving the overall performance of unsupervised learning-based methods.
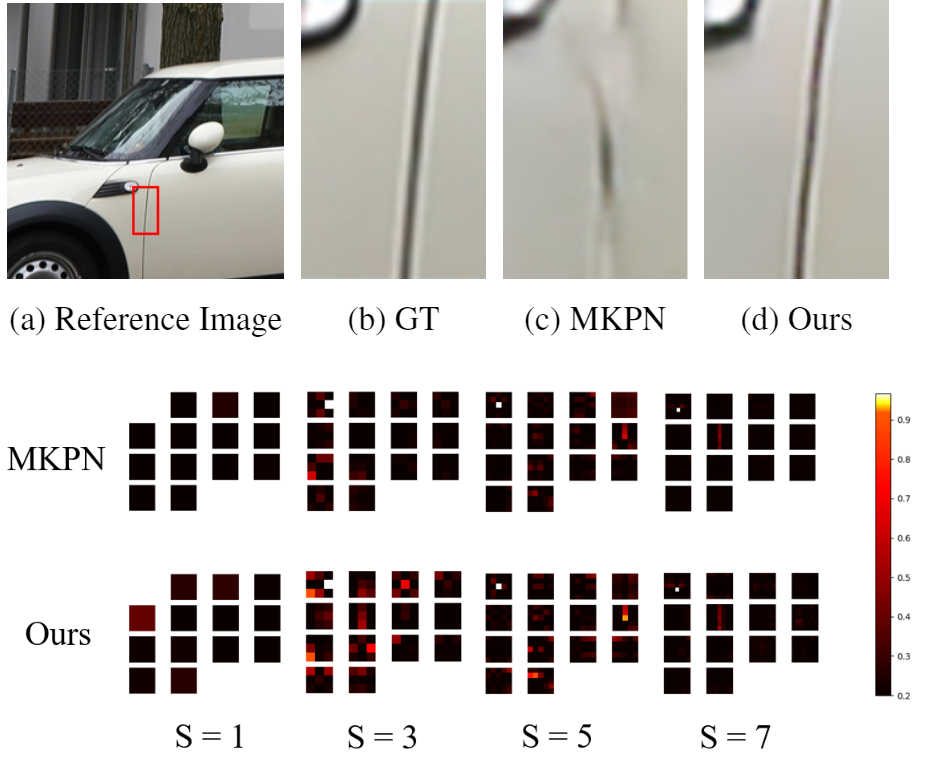

Burst image super-resolution is an ill-posed problem that aims to restore a high-resolution (HR) image from a se- quence of low-resolution (LR) burst images. To restore a photo-realistic HR image using their abundant information, it is essential to align each burst of frames containing ran- dom hand-held motion. Some kernel prediction networks (KPNs) that are operated without external motion compen- sation such as optical flow estimation have been applied to burst image processing as implicit image alignment mod- ules. However, the existing methods do not consider the interdependencies among the kernels of different sizes that have a significant effect on each pixel. In this paper, we propose a novel weighted multi-kernel prediction network (WMKPN) that can learn the discriminative features on each pixel for burst image super-resolution. Our experi- mental results demonstrate that WMKPN improves the vi- sual quality of super-resolved images. To the best of our knowledge, it outperforms the state-of-the-art within ker- nel prediction methods and multiple frame super-resolution (MFSR) on both the Zurich RAW to RGB and BurstSR datasets.
본 논문에서는 특징점 및 특징선 기반의 동시적 위치추정 및 지도작성(SLAM) 알고리즘을위한 퇴화(degeneracy) 방지 방법을 제안한다. 시각적 SLAM은 주로 특징점을 사용한다. 그러나 특징점을 사용하는 방법은 특징이 적은 환경 및 조도가 변하는 환경에서 강인하지 않다. 따라서 특징점의 약점을 보완하기 위해 특징선을 사용한다. 또한 특징점은 육안으로 식별 가능한 구조를 나타내지 못하여 작성된 지도를 알아보기 힘들다. 위의 한계를 극복하기 위해 이전 연구들에서는 특징선을 활발하게 사용했다. 그러나 특징선을 사용하는 과정에서 퇴화가 발생하기 때문에, 본 논문에서는 이를 해결하고자한다. 첫째, 우리는 퇴화가 발생한 특징선을 식별하는 간단한 방법을 제시한다. 또한 퇴화 문제를 피하기 위해 새로운 구조적 제한(constraint)을 제안한다. 마지막으로 강인한 광학 흐름 기반 특징선 추적 방법을 사용하는 특징선을 사용하는 SLAM 시스템을 구현한다. 실험에서는 EuRoC 데이터셋을 사용하여 결과를 입증하고, 다른 최신 알고리즘과 비교한다. 우리의 방법이 더 정확한 위치 인식 결과 및 지도 작성 결과를 가지는 것을 증명한다.
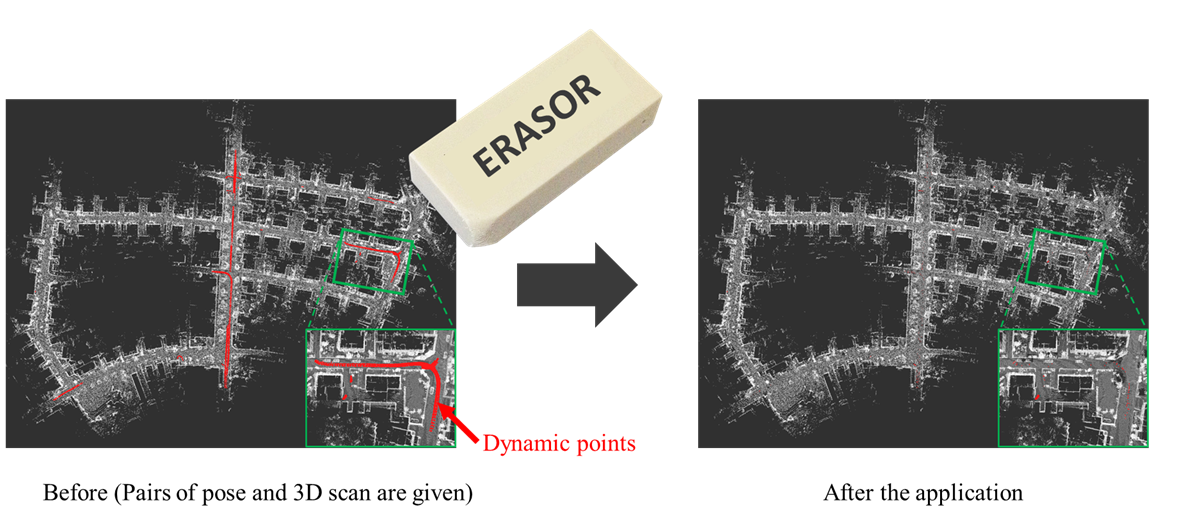
도심 환경에서 취득한 3D LiDAR 데이터에는 필연적으로 차량이나 보행자 같은 동적 물체에 대한 정보가 포함된다. 하지만 이러한 동적 물체에 대한 정보는 자율 주행 차량이나 모바일 로봇 같은 자율 주행 플랫폼이 주행(navigation)을 하거나 위치 인식(localization)을 할 때 방해 요인으로 작용한다. 왜냐하면 동적 물체는 일시적으로 공간을 차지하고 움직이기 때문에 실제로 해당 공간에 물체가 있지 않더라도 자율 주행 플랫폼 입장에서 물체가 있다고 인식하게 되기 때문이다. 따라서 본 논문에서는 맵 데이터 상에서 동적 물체만을 제거하여, 자율 주행 플랫폼이 주행을 하거나 위치 인식을 할 때 필요한 정적 물체들에 대한 정보만(static map)을 남기는 ERASOR라는 새로운 알고리즘을 제안한다. 포인트 클라우드의 각 포인트에 대해서 정적인가 동적인가를 따지는 기존의 알고리즘들과는 다르게, 바닥으로부터의 공간이 차지하고 있는 높이 차를 활용하여 pseudo occupancy라는 개념을 제안하였고, 동적 물체를 제거할 때도 해당 지역의 바닥 평면을 추출하여 동적 물체를 제거하는 Region-wise Ground Plane Fitting (R-GPF)라는 새로운 방식의 동적 물체 제거 방법을 제안하였다. 그 결과 기존의 방식들 대비 정적인 물체에 대한 정보는 더욱 더 많이 보존하면서 최소 10배 가량 빠르게 정적 맵을 생성할 수 있었다.
본 논문은 NVIDIA Jetson 플랫폼에서 수행한 다양한 Visual(-inertial) Odometry 알고리즘의 벤치마크 테스트를 제공한다. 비교된 알고리즘에는 모노 및 스테레오 알고리즘이 포함되며 다음의 Visual Odometry (VO) 및 Visual-Inertial Odometry (VIO)를 포함한다. (VIO) : VINS-Mono, VINS-Fusion, Kimera, ALVIO, Stereo-MSCKF, ORB-SLAM2 stereo 및 ROVIO. 이러한 알고리즘들은 주로 무인 항공기 (UAV) 에 사용되므로 프로세스 보드의 크기 및 하중이 제한된 상황에서도 잘 수행되어야 한다. NVIDIA에서 출시한 Jetson 보드는 이미지 처리를 원활하게 수행할 수 있는 강력한 중앙 처리 장치 (CPU) 와 그래픽 처리 장치 (GPU) 를 갖추고 있어 이러한 제약 조건을 충족한다. 그러나 기존 연구에서는 VO / VIO 를 실행하기 위한 처리 플랫폼으로서의 Jetson 보드 성능이 컴퓨팅 자원 사용 및 정확도 측면에서 폭넓게 비교되지 않았다. 따라서 본 연구에서는 여러 NVIDIA Jetson 플랫폼, 즉 NVIDIA Jetson TX2, Xavier NX, AGX Xavier에서 대표적인 VO / VIO 알고리즘의 성능을 비교하고 무인 항공기를 위한 새로운 데이터 세트 ‘KAIST VIO dataset’을 소개한다. 병진 운동이 없는 순수한 회전 운동을 포함하여, 이 데이터 세트에는 Visual(-inertial) Odometry에게 힘든 여러 기하학적 궤도가 있다. 성능 비교는 다양한 Jetson 보드, 알고리즘 및 궤적에서의 odometry 추정의 정확도, CPU 사용량 및 메모리 사용량 측면에 대해 수행된다. 우리는 포괄적인 벤치마크 테스트 결과를 제시하고 컴퓨터 비전 및 로봇 공학 애플리케이션을 위한 데이터 세트를 제시한다.
저자: 이상민, 김학구, 최대휘, 김형일, 노용만
Our work addresses long-term motion context issues for predicting future frames. To predict the future precisely, it is required to capture which long-term motion context (e.g., walking or running) the input motion (e.g., leg movement) belongs to. The bottlenecks arising when dealing with the long-term motion context are: (i) how to predict the long-term motion context naturally matching input sequences with limited dynamics, (ii) how to predict the long-term motion context with high-dimensionality (e.g., complex motion). To address the issues, we propose novel motion context-aware video prediction. To solve the bottleneck (i), we introduce a long-term motion context memory (LMC-Memory) with memory alignment learning. The proposed memory alignment learning enables to store long-term motion contexts into the memory and to match them with sequences including limited dynamics. As a result, the long-term context can be recalled from the limited input sequence. In addition, to resolve the bottleneck (ii), we propose memory query decomposition to store local motion context (i.e., low-dimensional dynamics) and recall the suitable local context for each local part of the input individually. It enables to boost the alignment effects of the memory. Experimental results show that the proposed method outperforms other sophisticated RNN-based methods, especially in long-term condition. Further, we validate the effectiveness of the proposed network designs by conducting ablation studies and memory feature analysis. The source code of this work is available.

Figure 1. Memory alignment learning with long-term motion context memory
우리 학부 장동의 교수님께서 2020 한국인공지능학회 학술혁신상을 수상하셨습니다.
한국인공지능학회(학회장: 유창동)는 2020년 한해동안의 인공지능 관련 연구성과를 돌아보는 시상식을 성남-KAIST 차세대 ICT혁신센터에서 가졌습니다.
금년도 학술혁신상 수상자로, 딥 러닝의 수리적 이해 및 드론 자율비행 연구로 훌륭한 성과를 낸 우리 학부 장동의 교수님이 선정되셨습니다. 또한 추계학술대회 포스터 우수논문으로 장동의 교수님 지도하는 Xiaowei Xing 박사과정생의 프로그래밍툴박스 연구가 선정되었습니다.
한편 하계학술대회 10편 우수논문으로는 유창동 교수님 연구실 김준영 박사과정생, 신진우 교수님 연구실 남주현 박사과정생 그리고 윤찬현 교수님 연구실 졸업생 Duc Canh Le 석사의 논문이 선정되었습니다.
이번 시상식은 한국인공지능학회에서 이룬 성과들을 보여주고 한국의 인공지능 발전을 위해서 학회 회원 및 연구자들의 사기를 높이고 그 발전을 독려하는 뜻깊은 행사로 되었습니다.
장동의 교수님 외 수상하신 모든 분들께 축하의 인사를 드립니다.
우리 학부 명현 교수님께서 2020년도 한국로봇학회 특별상(KRI상) 수상자로 선정되셨습니다. 시상식은 지난 4일 온라인으로 개최된 2020년도 한국로봇학회 정기총회에서 열렸습니다.
KRI(KROS Robotics Innovation)상은 한국로봇학회에서 로봇 분야의 혁신적 업적을 낸 연구자를 격려하여 관련 분야의 발전을 이루고자 작년부터 새롭게 제정한 상입니다. 올해의 수상자로는 우리 학부 명현 교수님과 서울대학교 조규진 교수님께서 선정되셨습니다. 명현 교수님께서는 지상, 수중, 지하 등 다양한 환경의 로봇에 대한 자율 항법 기술, 극한 환경 로봇 기술 등 필드 로봇 분야의 혁신적인 업적을 성취하여 로봇 기술 발전에 큰 공로를 기여하였기에 해당 상을 수상하셨습니다.
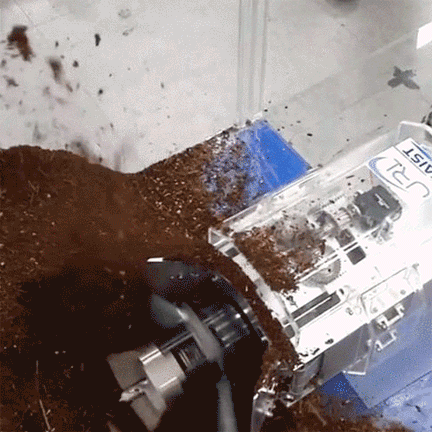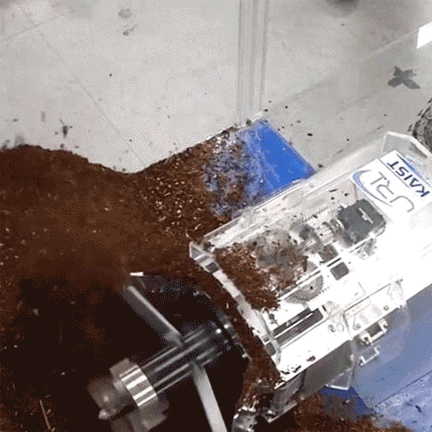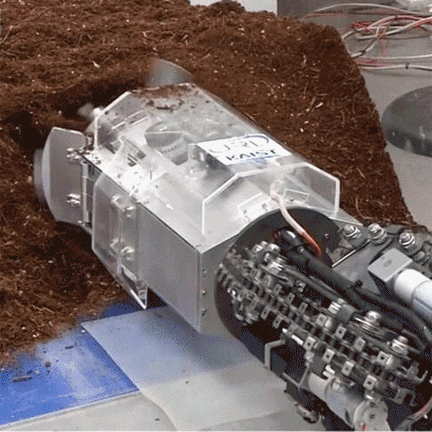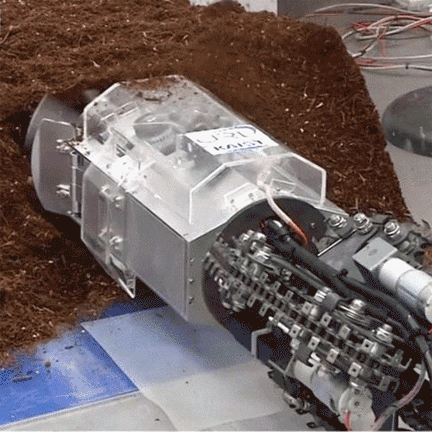
특히 올해 여름, 명현 교수님 연구팀이 개발한 지하 탐사 로봇(Mole-bot)은 국내외 유수 언론사의 주목을 받았습니다. 아래의 링크를 클릭하시면 공과대학교 Research Webzine 2020 Fall호에 게재된 관련 연구성과를 만나보실 수 있습니다.
다시 한 번, 올해 우수한 성과를 달성하여 전기및전자공학부의 위상을 드높인 명현 교수님께 축하의 인사를 보내드립니다.
http://breakthroughs.kaist.ac.kr/?post_no=1731