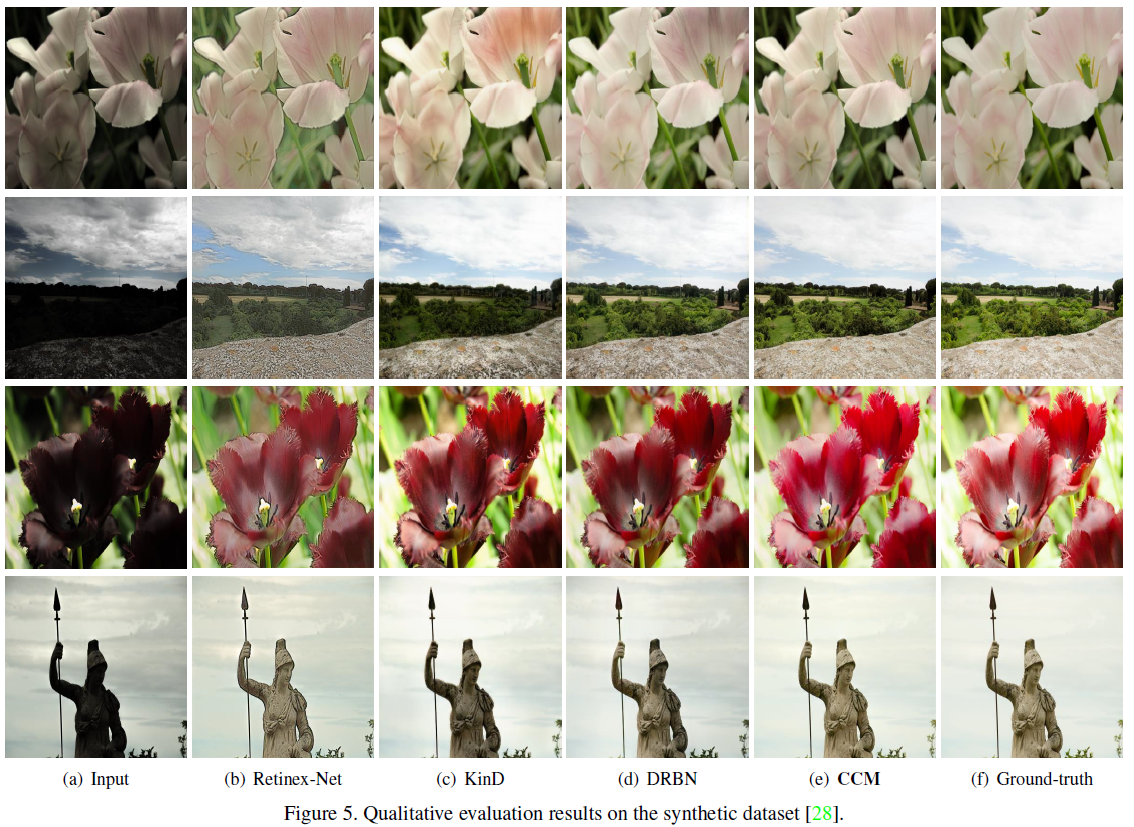
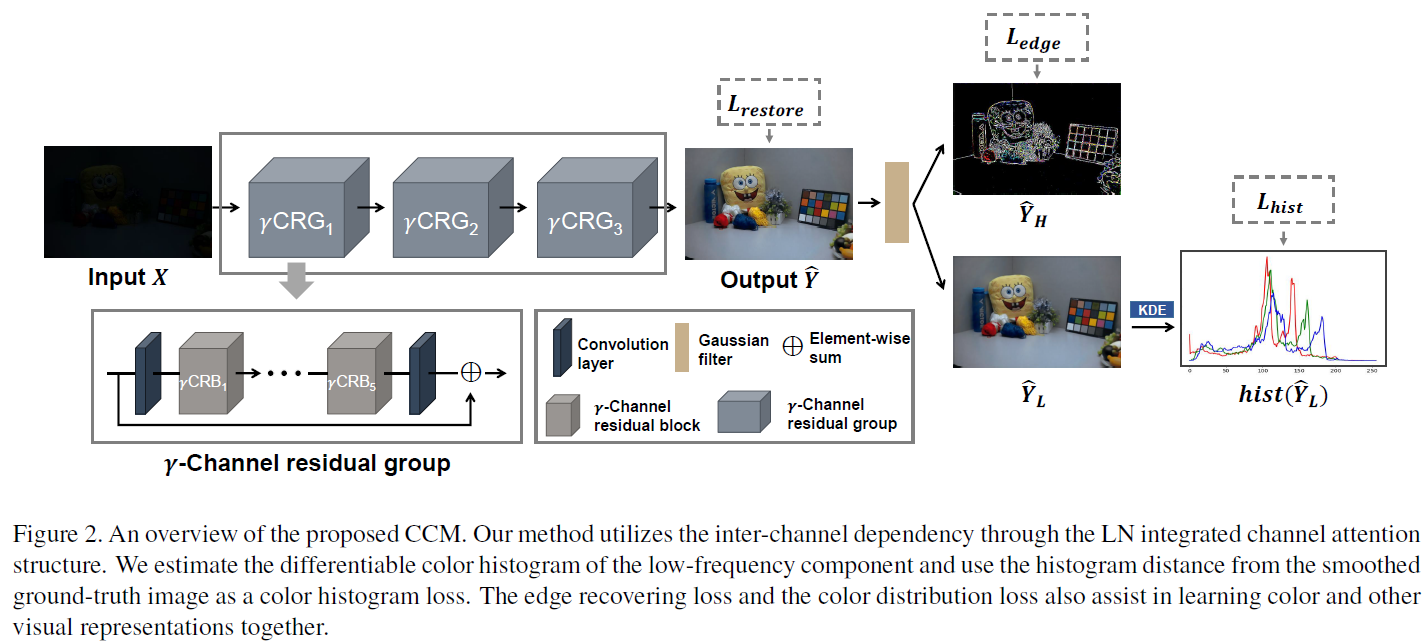

Color conveys important information about the visible world. However, under low-light conditions, both pixel intensity, as well as true color distribution, can be significantly shifted. Moreover, most of such distortions are non-recoverable due to inverse problems. In the present study, we utilized recent advancements in learning-based methods for low-light image enhancement. However, while most “deep learning” methods aim to restore high-level and object-oriented visual information, we hypothesized that learning-based methods can also be used for restoring color-based information. To address this question, we propose a novel color representation learning method for low-light image enhancement. More specifically, we used a channel-aware residual network and a differentiable intensity histogram to capture color features. Experimental results using synthetic and natural datasets suggest that the proposed learning scheme achieves state-of-the-art performance. We conclude from our study that inter-channel dependency and color distribution matching are crucial factors for learning color representations under low-light conditions.