Abstract:
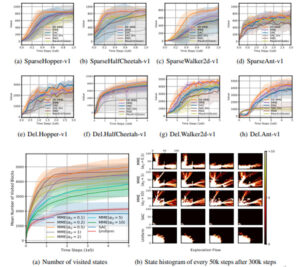
본 논문에서는 모델이 없는 샘플 기반 학습에서 최대 엔트로피 강화학습을 구현하는 SAC 알고리듬의 한계를 극복하기 위해 강화 학습을 위한 최대 최소 엔트로피 프레임워크를 제안한다.
최대 엔트로피 강화학습은 미래에 엔트로피가 높은 상태에 도달하기 위한 정책에 대한 학습을 안내하는 반면, 제안된 최대-최소 엔트로피 프레임워크는 엔트로피가 낮은 상태를 방문하고 이러한 낮은 엔트로피 상태의 엔트로피를 최대화하여 더 나은 탐사를 촉진하는 것을 목표로 한다.
일반 마르코프 의사 결정 프로세스의 경우, 탐색과 착취의 분리를 기반으로 제안된 최대-최소 엔트로피 프레임워크에 따라 효율적인 알고리듬이 구성된다.
수치 결과는 제안된 알고리듬이 현재 최첨단 강화학습 알고리듬보다 성능이 크게 향상되었음을 보여준다.
Abstract:
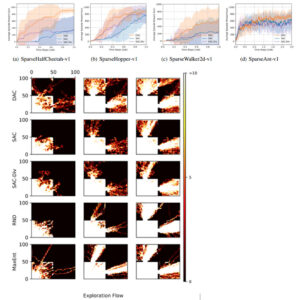
본 논문에서는 더 나은 탐색을 위해 기존의 정책 엔트로피 정규화를 강화하기 위해 샘플 인식 정책 엔트로피 정규화를 제안한다.
재생 버퍼에서 얻을 수 있는 샘플 분포를 활용하여 제안된 샘플 인식 엔트로피 정규화는 샘플 효율적인 탐색을 위해 정책 동작 분포와 재생 버퍼에서 샘플 동작 분포의 가중 합계의 엔트로피를 최대화한다.
제안된 샘플 인식 엔트로피 정규화를 통해 목적 함수에 정책 반복을 적용하여 다양성 행위자-비판(DAC)이라는 실제 알고리듬을 개발한다.
수치 결과는 DAC가 강화 학습을 위한 기존 최신 알고리듬을 크게 능가한다는 것을 보여준다.
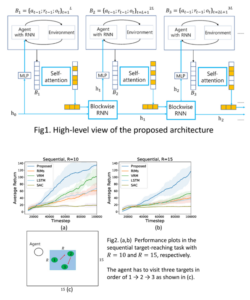
Title: Blockwise Sequential Model Learning for Partially Observable Reinforcement Learning
Authors: Giseung Park, Sungho Choi, Youngchul Sung
Presented at AAAI 2022 (Oral Presentation).
Abstract:
This paper proposes a new sequential model learning architecture to solve partially observable Markov decision problems. Rather than compressing sequential information at every timestep as in conventional recurrent neural network-based methods, the proposed architecture generates a latent variable in each data block with a length of multiple timesteps and passes the most relevant information to the next block for policy optimization. The proposed blockwise sequential model is implemented based on self-attention, making the model capable of detailed sequential learning in partial observable settings. The proposed model builds an additional learning network to efficiently implement gradient estimation by using self-normalized importance sampling, which does not require the complex blockwise input data reconstruction in the model learning. Numerical results show that the proposed method significantly outperforms previous methods in various partially observable environments.
Authors: Y. Ro, K. Lee, S. E. Whang and C. Suh
Venue: NeurIPS 2021
Title: Sample selection for fair and robust training
Abstract: Fairness and robustness are critical elements of Trustworthy AI that need to be addressed together. Fairness is about learning an unbiased model while robustness is about learning from corrupted data, and it is known that addressing only one of them may have an adverse affect on the other. In this work, we propose a sample selection-based algorithm for fair and robust training. To this end, we formulate a combinatorial optimization problem for the unbiased selection of samples in the presence of data corruption. Observing that solving this optimization problem is strongly NP-hard, we propose a greedy algorithm that is efficient and effective in practice. Experiments show that our algorithm obtains fairness and robustness that are better than or comparable to the state-of-the-art technique, both on synthetic and benchmark real datasets. Moreover, unlike other fair and robust training baselines, our algorithm can be used by only modifying the sampling step in batch selection without changing the training algorithm or leveraging additional clean data.

Authors: S. Kim, M. Jang and C. Suh
Venue: RecSys (ComplexRec) 2021
Title: Group match prediction via neural networks
Abstract: We consider the group match prediction problem where the goal is to estimate the probability of one group of items preferred over another, based on partially observed group comparison data. Most prior algorithms, each tailored to a specific statistical model, suffer from inconsistent performances across different scenarios. Motivated by a key common structure of the state-of-the-art, which we call the reward-penalty structure, we develop a unified framework that achieves consistently high performances across a wide range of scenarios. Our distinction lies in introducing neural networks embedded with the reward-penalty structure. Extensive experiments on synthetic and real-world datasets show that our framework consistently leads to the best performance, while the state-of-the-art perform inconsistently.
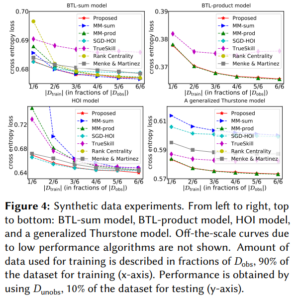
Authors: G. Suh, S. Jeon and C. Suh
Venue: IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT) 2021
Title: When to use graph side information in matrix completion
Abstract: We consider a matrix completion problem that leverages graph as side information. One common approach in recently developed efficient algorithms is to take a two-step procedure: (i) clustering communities that form the basis of the graph structure; (ii) exploiting the estimated clusters to perform matrix completion together with iterative local refinement of clustering. A major limitation of the approach is that it achieves the information-theoretic limit on the number of observed matrix entries, promised by maximum likelihood estimation, only when a sufficient amount of graph side information is provided (the quantified measure is detailed later). The contribution of this work is to develop a computationally efficient algorithm that achieves the optimal sample complexity for the entire regime of graph information. The key idea is to make a careful selection for the information employed in the first clustering step, between two types of given information: graph & matrix ratings. Our experimental results conducted both on synthetic and real data confirm the superiority of our algorithm over the prior approaches in the scarce graph information regime.

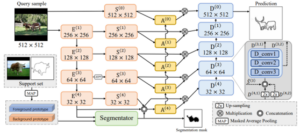
We tackle a novel few-shot learning challenge, few-shot semantic edge detection, aiming to localize boundaries of novel categories using only a few labeled samples. Reliable boundary information has been shown to boost the performance of semantic segmentation and localization, while also playing a key role in its own right in object reconstruction, image generation and medical imaging. However, existing semantic edge detection techniques require a large amount of labeled data to train a model. To overcome this limitation, we present Class-Agnostic Few-shot Edge detection Network (CAFENet) based on a meta-learning strategy. CAFENet employs a semantic segmentation module in small-scale to compensate for the lack of semantic information in edge labels. To effectively fuse the semantic information and low-level cues, CAFENet also utilizes an attention module which dynamically generates multi-scale attention map, as well as a novel regularization method that splits high-dimensional features into several low-dimensional features and conducts multiple metric learning. Since there are no existing datasets for few-shot semantic edge detection, we construct two new datasets, FSE-1000 and SBD5 i , and evaluate the performance of the proposed CAFENet on them. Extensive simulation results confirm that CAFENet achieves better performance compared to the baseline methods using fine-tuning or few-shot segmentation.
In federated learning (FL), a number of distributed clients targeting the same task collaborate to train a single global model without sharing their data. The learning process typically starts from a randomly initialized or some pretrained model. In this paper, we aim at designing an initial model based on which an arbitrary group of clients can obtain a global model for its own purpose, within only a few rounds of FL. The key challenge here is that the downstream tasks for which the pretrained model will be used are generally unknown when the initial model is prepared. Our idea is to take a meta-learning approach to construct the initial model so that any group with a possibly unseen task can obtain a high-accuracy global model within only R rounds of FL. Our meta-learning itself could be done via federated learning among willing participants and is based on an episodic arrangement to mimic the R rounds of FL followed by inference in each episode. Extensive experimental results show that our method generalizes well for arbitrary groups of clients and provides large performance improvements given the same overall communication/computation resources, compared to other baselines relying on known pretraining methods.

While federated learning (FL) allows efficient model training with local data at edge devices, among major issues still to be resolved are: slow devices known as stragglers and malicious attacks launched by adversaries. While the presence of both of these issues raises serious concerns in practical FL systems, no known schemes or combinations of schemes effectively address them at the same time. We propose Sageflow, staleness-aware grouping with entropy-based filtering and loss-weighted averaging, to handle both stragglers and adversaries simultaneously. Model grouping and weighting according to staleness (arrival delay) provides robustness against stragglers, while entropy-based filtering and loss-weighted averaging, working in a highly complementary fashion at each grouping stage, counter a wide range of adversary attacks. A theoretical bound is established to provide key insights into the convergence behavior of Sageflow. Extensive experimental results show that Sageflow outperforms various existing methods aiming to handle stragglers/adversaries.
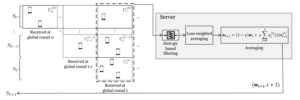
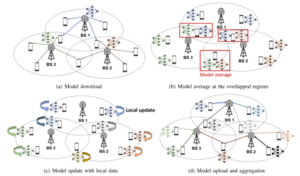
We consider federated learning (FL) with multiple wireless edge servers having their own local coverage. We focus on speeding up training in this increasingly practical setup. Our key idea is to utilize the clients located in the overlapping coverage areas among adjacent edge servers (ESs); in the model-downloading stage, the clients in the overlapping areas receive multiple models from different ESs, take the average of the received models, and then update the averaged model with their local data. These clients send their updated model to multiple ESs by broadcasting, which acts as bridges for sharing the trained models between servers. Even when some ESs are given biased datasets within their coverage regions, their training processes can be assisted by adjacent servers through the clients in their overlapping regions. As a result, the proposed scheme does not require costly communications with the central cloud server (located at the higher tier of edge servers) for model synchronization, significantly reducing the overall training time compared to the conventional cloud-based FL systems. Extensive experimental results show remarkable performance gains of our scheme compared to existing methods. Our design targets latency-sensitive applications where edge-based FL is essential, e.g., when a number of connected cars/drones must cooperate (via FL) to quickly adapt to dynamically changing environments.