저널: Advanced Intelligent Systems
Title: Highly reliable synaptic cell array based on organic-inorganic hybrid bilayer stack toward precise offline learning
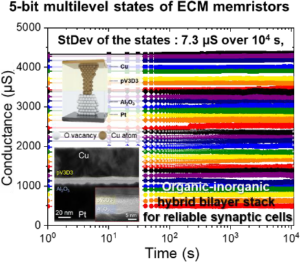
Abstract: As the use of artificial intelligence soars, development of novel neuromorphic computing is highly important because of disadvantages of the existing von Neumann architecture. In addition, extensive research on electrochemical metallization (ECM) memristors as synaptic cells have been carried out in pursuit of a linear conductance update for online learning applications. In most cases, however, a conductance distribution change during retention time while updating has not been studied as a major issue, giving less consideration for inference-only computing accelerators based on offline learning. Herein, we suggest organic-inorganic bilayer stacking for synaptic unit cells using poly(1,3,5-trivinyl-1,3,5-trimethyl cyclotrisiloxane) (pV3D3) and Al2O3 thin films, showing highly enhanced reliability for offline learning. The bilayer structure achieved better reliability and control of the analog resistive switching and synaptic functions, respectively, through the guided formation of conductive filaments via tip enhanced electric fields. In addition, 5-bit multilevel states achieved long-term stability (> 104 s) following an in-depth study on conductance-level stability. Finally, a device to-system-level simulation was performed by building a CNN based on the hybrid devices. This highlighted the significance of multilevel states in fully connected layers. We believe that our study provides a practical approach to using ECM-based memristors for inference-only neural network accelerators.