Abstract
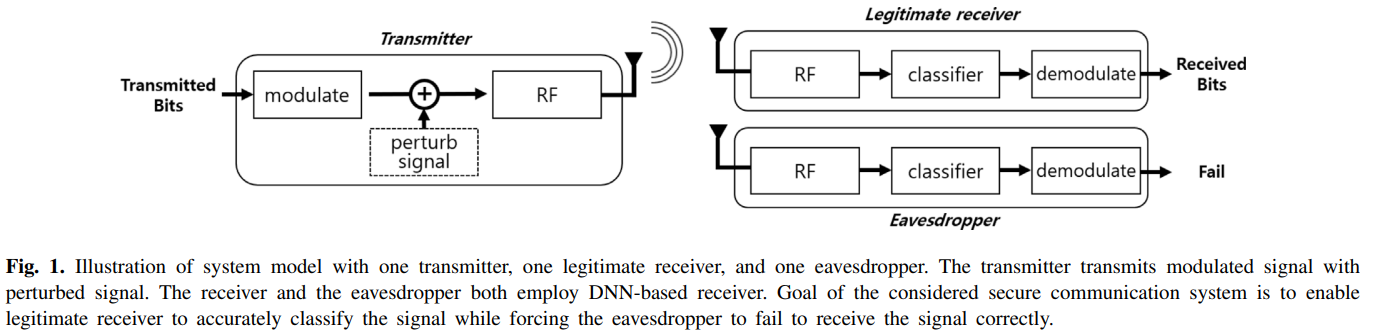
This paper considers wireless communication system consisted of one transmitter, one legitimate receiver, and one eavesdropper. The transmitter transmits perturbation-added signal (i.e. adversarial example) with a certain modulation type, while the legitimate receiver and the eavesdropper adopt deep neural networks (DNN)-based classifier to recognize the modulation type of the received signal. Compared to the fact that the general goal of adversarial examples being a misclassification of all available classifiers, our objective is to design an adversarial example that lets the legitimate receiver classify accurately while the eavesdropper misclassifies. To this end, we propose two design approaches of the adversarial examples: (i) A priori; (ii) A posteriori, i.e. before and after learning steps of the receiver, respectively. Numerical results show that both approaches are effective for securing the communication link. The Korean Institute of Communications and Information Sciences (KICS). Publishing services by Elsevier B.V. This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).