The research study authored by Joon-Ki Hong* (KAIST EE), Soon-Il Kwon* (SNUH), Eue-Keun Choi (SNUH), Eui-Jae Lee (SNUH), David Earl Hostallero (KAIST EE), Wan-Ju Kang (KAIST EE), Byung-Hwan Lee (Skylabs), Eui-Rim Jeong (Hanbat University), Bon-Kwon Koo (SNUH), Se-Il Oh (SNUH), Yung Yi (KAIST EE) was accepted at JMIR mHealth and uHealth 7.6(2019)
Title: Deep Learning Approaches to Detect Atrial Fibrillation Using Photoplethysmographic Signals: Algorithms Development Study
Authors: Joon-Ki Hong*, Soon-Il Kwon*, Eue-Keun Choi, Eui-Jae Lee, David Earl Hostallero, Wan Ju Kang, Byung-Hwan Lee, Eui-Rim Jeong, Bon-Kwon Koo, Se-Il Oh, Yung Yi (* these authors contributed equally)
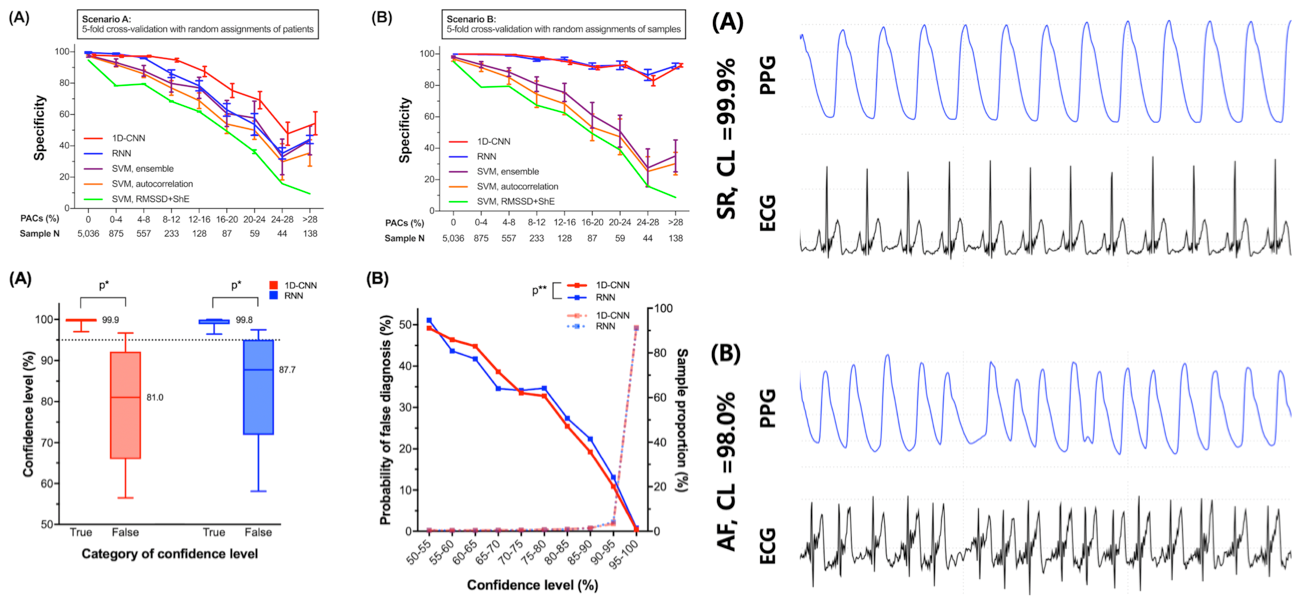
Wearable devices have evolved as screening tools for atrial fibrillation (AF). A photoplethysmographic (PPG) AF detection algorithm was developed and applied to a convenient smartphone-based device with good accuracy. However, patients with paroxysmal AF frequently exhibit premature atrial complexes (PACs), which result in poor unmanned AF detection, mainly because of rule-based or handcrafted machine learning techniques that are limited in terms of diagnostic accuracy and reliability. We developed deep learning (DL) based AF classifiers based on 1-dimensional convolutional neural network (1D-CNN) and recurrent neural network (RNN) architectures and examined 75 patients with AF who underwent successful elective direct-current cardioversion (DCC). New DL classifiers could detect AF using PPG monitoring signals with high diagnostic accuracy (97.58 %) even with frequent PACs and could outperform previously developed AF detectors. Although diagnostic performance decreased as the burden of PACs increased, performance improved when samples from more patients were trained. Moreover, the reliability of the diagnosis could be indicated by the confidence level (CL). Wearable devices sensing PPG signals with DL classifiers should be validated as tools to screen for AF.