The paper “Neural Adaptive Content-aware Internet Video Delivery” (Author Hyunho Yeo, Youngmok Jung, Jaehong Kim, Jin Woo Shin and Dongsu Han) of Ph.D. Student Hyunho Yeo (Advisor: Dongsu Han), will be adopted at USENIX Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation (OSDI) October, 2018.
USENIX OSDI is a flagship conference in the field of Operating Systems, held every two years, with about 30-40 papers published each time. It is famous for presenting research and innovative technologies such as Google’s flagship system MapReduce (2004, citation = 25,000), BigTable (2006, citation = 5,800), TensorFlow (2016, citation = 5,300), and others. Especially, this issue is meaningful in the fact that it was the first paper of KAIST in the history of 26 years of OSDI society and adopted in Korean institution in 10 years.
This study is based on the position paper “How will Deep Learning Change Internet Video Delivery? (ACM HotNets 2017, First author Hyunho Yeo) collaborated with Deep Learning Expert Jin-woo Shin to present a new design that combines adaptive streaming and deep learning technology, the core technologies of Internet video transmission.
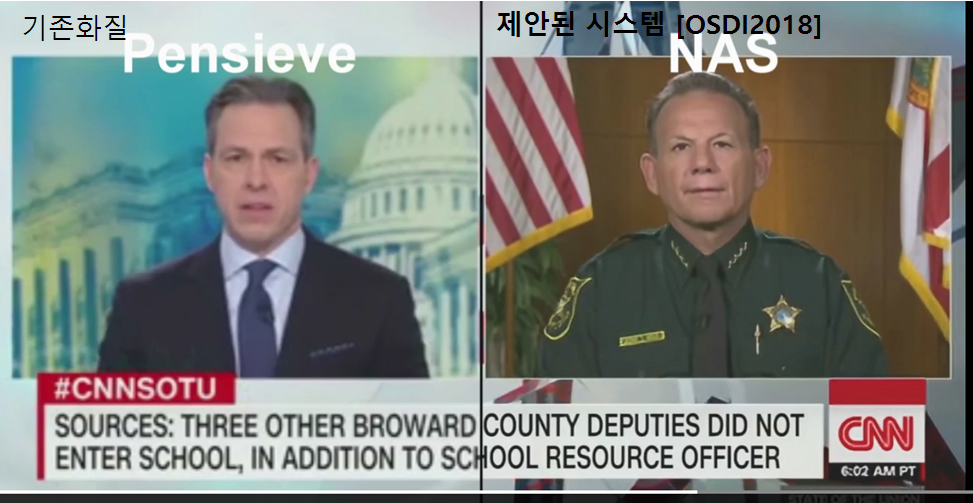
In this paper, we propose an HTTP adaptive streaming system based on super-resolution DNN (Deep Neural Network) and re-implementation DASH player, dramatically improving the quality of User Experience (more than 50%) compared to the existing one. For this, the client is designed to enable real-time inference, and the design that transmits the DNN model for each individual video is operated in conjunction with the existing MPEG DASH.
In this study, we applied the DNN to the video content itself for the first time to prepare for the research on the video transmission and the network of the distribution network (Content Distribution Network). We propose content-awareness of DNNs, implement the system practically, and acknowledge innovation that demonstrates its advantages in a real environment.