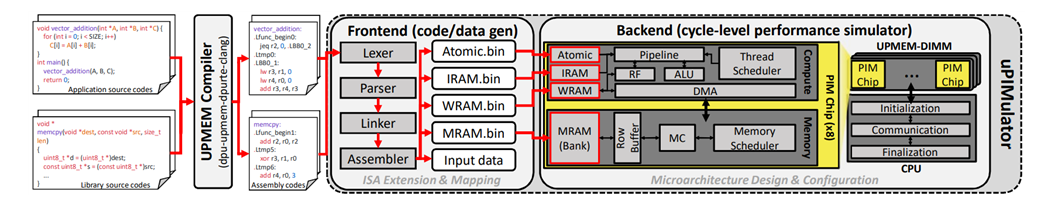
Professor Yang-Kyu Choi’s Research Team Solved Computing Challenges with Neuromorphic Neural Networks

*Graph coloring problem: A term used in graph theory, requiring different colors to be assigned to each vertex of a graph. This is similar to assigning frequencies to broadcasting stations to prevent overlap and the creation of areas with poor reception, and is widely applied in various fields.
The research team announced on the 3rd that they have developed a neuromorphic oscillatory neural network that mimics the interactions of biological neurons using silicon varistor components.
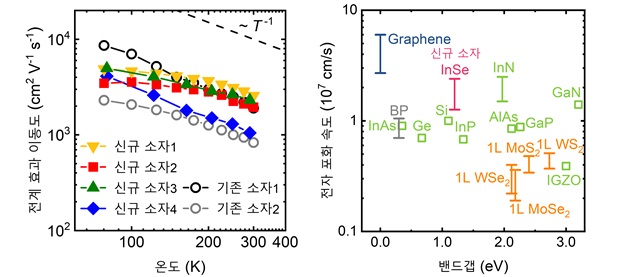
With the arrival of the big data era, artificial intelligence technology has made significant progress. One of the neuromorphic computing methods, the oscillatory neural network (oscillatory neural network), is an artificial neural network that mimics the interaction of neurons. The oscillatory neural network uses the connection operations of oscillators, which are the basic units, and performs calculations using oscillations rather than the magnitude of signals, thus offering advantages in terms of power consumption.
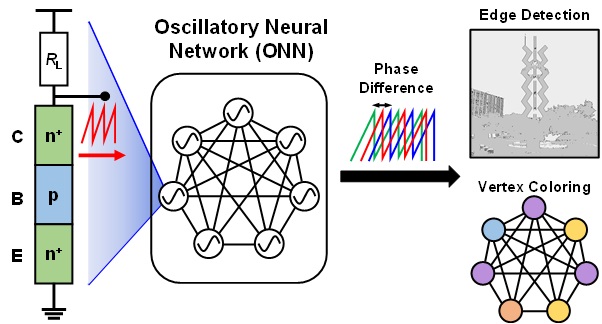
The research, led by Seong-Yun Yun, a doctoral student, and Professor Joon-Kyu Han from Sogang University, stated, “The developed oscillatory neural network can be used as neuromorphic computing hardware capable of calculating complex computing challenges, and is expected to be useful in resource allocation, new drug development, semiconductor circuit design, and scheduling,” highlighting the significance of the research.
The study, co-authored by Seong-Yun Yun and Professor Joon-Kyu Han, was published in ‘Nano Letters’, in its 24th volume, issue 9, on March 2024, and was selected as a supplementary cover article.

This research was conducted with the support of the Korea Research Foundation’s Next-Generation Intelligent Semiconductor Technology Development Project and the National Semiconductor Research Laboratory Support Core Technology Development Project.






![연구 > 연구성과 16 [Professor Rhu Minsoo’s team wins the Best Paper Award’ at the International Symposium on High-Performance Computer Architecture (HPCA)]](https://ee.kaist.ac.kr/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/IMG_0100.png)