Title: Rank-1 Matrix Completion with Gradient Descent and Small Random Initialization
Authors: Daesung Kim, Hye Won Chung
Conference: Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2023.
Abstract:
The nonconvex formulation of the matrix completion problem has received significant attention in recent years due to its affordable complexity compared to the convex formulation. Gradient Descent (GD) is a simple yet efficient baseline algorithm for solving nonconvex optimization problems. The success of GD has been witnessed in many different problems in both theory and practice when it is combined with random initialization. However, previous works on matrix completion require either careful initialization or regularizers to prove the convergence of GD. In this paper, we study the rank-1 symmetric matrix completion and prove that GD converges to the ground truth when small random initialization is used. We show that in a logarithmic number of iterations, the trajectory enters the region where local convergence occurs. We provide an upper bound on the initialization size that is sufficient to guarantee the convergence, and show that a larger initialization can be used as more samples are available. We observe that the implicit regularization effect of GD plays a critical role in the analysis, and for the entire trajectory, it prevents each entry from becoming much larger than the others.
Figure:
Title: A Worker-Task Specialization Model for Crowdsourcing: Efficient Inference and Fundamental Limits
Authors: Doyeon Kim, Jeonghwan Lee, Hye Won Chung
Journal: IEEE Transaction on Information Theory, 2024.
Abstract:
Crowdsourcing system has emerged as an effective platform for labeling data with relatively low cost by using non-expert workers. Inferring correct labels from multiple noisy answers on data, however, has been a challenging problem, since the quality of the answers varies widely across tasks and workers. Many existing works have assumed that there is a fixed ordering of workers in terms of their skill levels, and focused on estimating worker skills to aggregate the answers from workers with different weights. In practice, however, the worker skill changes widely across tasks, especially when the tasks are heterogeneous. In this paper, we consider a new model, called d-type specialization model, in which each task and worker has its own (unknown) type and the reliability of each worker can vary in the type of a given task and that of a worker. We allow that the number d of types can scale in the number of tasks. In this model, we characterize the optimal sample complexity to correctly infer the labels within any given accuracy, and propose label inference algorithms achieving the order-wise optimal limit even when the types of tasks or those of workers are unknown. We conduct experiments both on synthetic and real datasets, and show that our algorithm outperforms the existing algorithms developed based on more strict model assumptions.
Figure:
Title: Efficient Algorithms for Exact Graph Matching on Correlated Stochastic Block Models with Constant Correlation
Authors: Joonhyuk Yang, Dongpil Shin, Hye Won Chung
Conference: The International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 2023
Abstract:
We consider the problem of graph matching, or learning vertex correspondence, between two correlated stochastic block models (SBMs). The graph matching problem arises in various fields, including computer vision, natural language processing and bioinformatics, and in particular, matching graphs with inherent community structure has significance related to de-anonymization of correlated social networks. Compared to the correlated Erdos-Renyi (ER) model, where various efficient algorithms have been developed, among which a few algorithms have been proven to achieve the exact matching with constant edge correlation, no low-order polynomial algorithm has been known to achieve exact matching for the correlated SBMs with constant correlation. In this work, we propose an efficient algorithm for matching graphs with community structure, based on the comparison between partition trees rooted from each vertex, by extending the idea of Mao et al. (2021) to graphs with communities. The partition tree divides the large neighborhoods of each vertex into disjoint subsets using their edge statistics to different communities. Our algorithm is the first low-order polynomial-time algorithm achieving exact matching between two correlated SBMs with high probability in dense graphs.
Figure:
Title: Recovering Top-Two Answers and Confusion Probability in Multi-Choice Crowdsourcing
Authors: Hyeonsu Jeong, Hye Won Chung
Conference: The International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 2023
Abstract:
Crowdsourcing has emerged as an effective platform for labeling large amounts of data in a cost- and time-efficient manner. Most previous work has focused on designing an efficient algorithm to recover only the ground-truth labels of the data. In this paper, we consider multi-choice crowdsourcing tasks with the goal of recovering not only the ground truth, but also the most confusing answer and the confusion probability. The most confusing answer provides useful information about the task by revealing the most plausible answer other than the ground truth and how plausible it is. To theoretically analyze such scenarios, we propose a model in which there are the top two plausible answers for each task, distinguished from the rest of the choices. Task difficulty is quantified by the probability of confusion between the top two, and worker reliability is quantified by the probability of giving an answer among the top two. Under this model, we propose a two-stage inference algorithm to infer both the top two answers and the confusion probability. We show that our algorithm achieves the minimax optimal convergence rate. We conduct both synthetic and real data experiments and demonstrate that our algorithm outperforms other recent algorithms. We also show the applicability of our algorithms in inferring the difficulty of tasks and in training neural networks with top-two soft labels.
Figure:
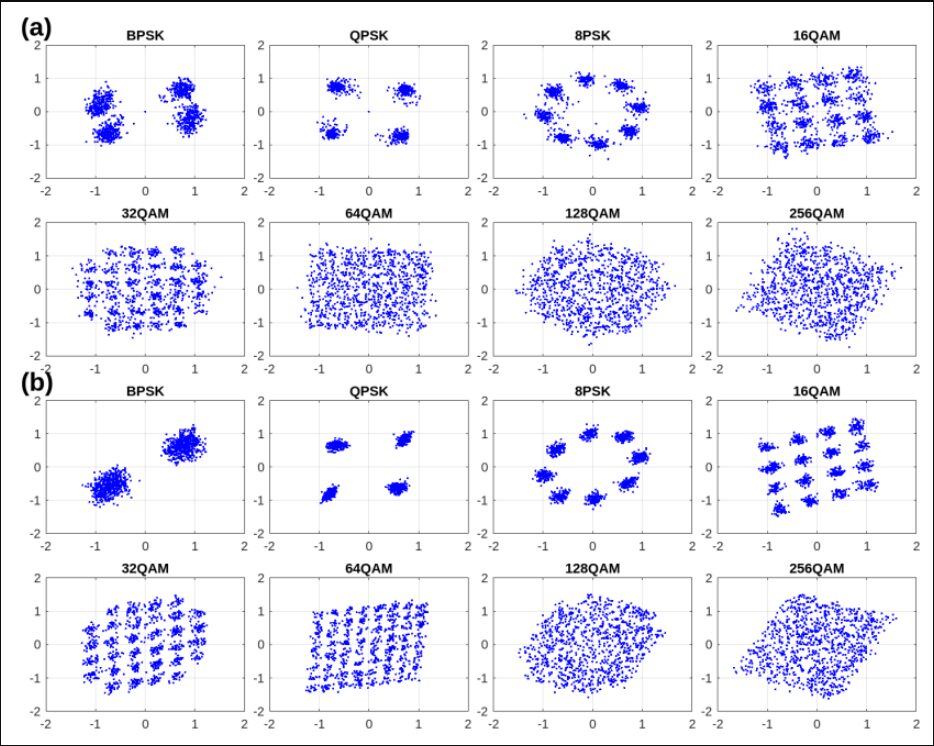
Abstract : Modulation classification (MC) is the first step performed at the receiver side unless the modulation type is explicitly indicated by the transmitter. Machine learning techniques have been widely used for MC recently. In this paper, we propose a novel MC technique dubbed as Joint Equalization and Modulation Classification based on Constellation Network (EMC2-Net). Unlike prior works that considered the constellation points as an image, the proposed EMC2-Net directly uses a set of 2D constellation points to perform MC. In order to obtain clear and concrete constellation despite multipath fading channels, the proposed EMC2-Net consists of equalizer and classifier having separate and explainable roles via novel three-phase training and noise-curriculum pretraining. Numerical results with linear modulation types under different channel models show that the proposed EMC2-Net achieves the performance of state-of-the-art MC techniques with significantly less complexity.
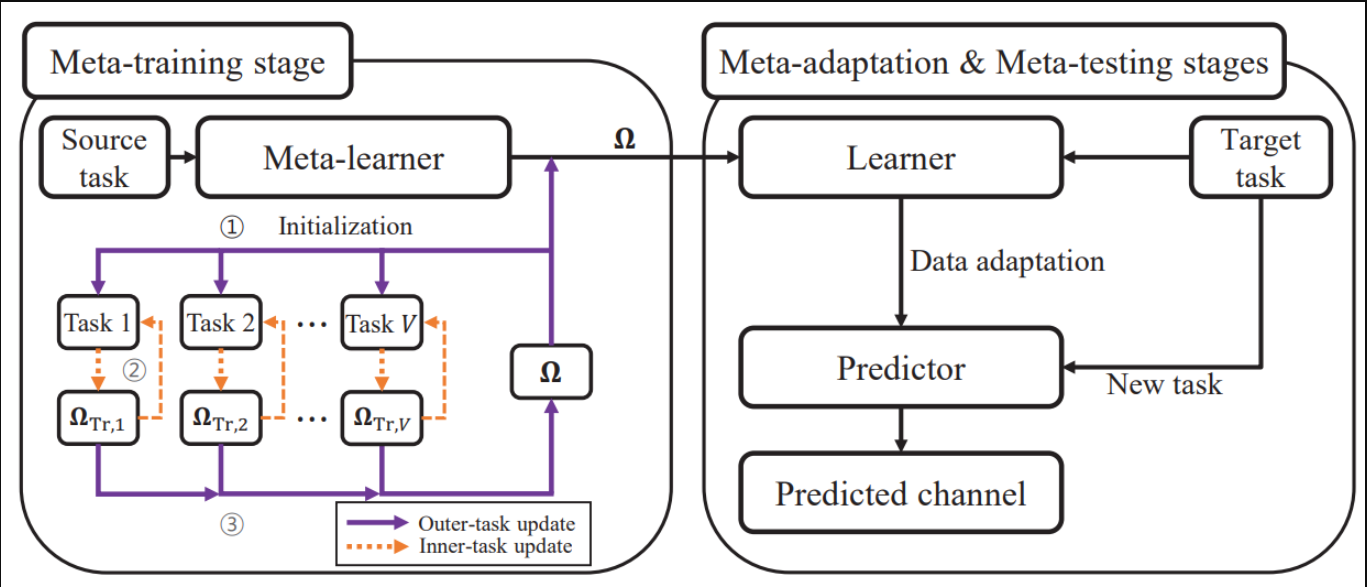
Abstract : Accurate channel knowledge is critical in massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO), which motivates the use of channel prediction. Machine learning techniques for channel prediction hold much promise, but current schemes are limited in their ability to adapt to changes in the environment because they require large training overheads. To accurately predict wireless channels for new environments with reduced training overhead, we propose a fast adaptive channel prediction technique based on a meta-learning algorithm for massive MIMO communications. We exploit the model-agnostic meta-learning (MAML) algorithm to achieve quick adaptation with a small amount of labeled data. Also, to improve the prediction accuracy, we adopt the denoising process for the training data by using deep image prior (DIP). Numerical results show that the proposed MAML-based channel predictor can improve the prediction accuracy with only a few fine-tuning samples in various scenarios. The DIP-based denoising process gives an additional gain in channel prediction, especially in low signal-to-noise ratio regimes.
Authors: Mohammadmahdi Rahimi, Younghyun Park, Humaira Kousar, Hasnain Bhatti, Jaekyun Moon
Conference: Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS) 2023
Abstract:
Federated Learning (FL) is a decentralized machine learning paradigm that enables collaborative model training across dispersed nodes without having to force individual nodes to share data.However, its broad adoption is hindered by the high communication costs of transmitting large model parameters. This paper presents EvoFed, a novel approach that integrates Evolutionary Strategies (ES) with FL to address these challenges.EvoFed employs a concept of ‘fitness-based information sharing’, deviating significantly from the conventional model-based FL. Rather than exchanging the actual updated model parameters, each nodetransmits a distance-based similarity measure between the locally updated model and each member of the noise-perturbed model population. Each node, as well as the server, generates an identical population set of perturbed models in a completely synchronized fashion using the same random seeds. With properly chosen noise variance and population size, certain perturbed models will closely reflect the actual model updated using the local dataset, allowing the transmitted similarity measures (or fitness values) to carry nearly the full information about the model parameters.As the size of the population is typically much smaller than the number of model parameters, the savings in communication load is large. The server aggregates these fitness values, weightedby the client’s batch sizes, and is able to update the global model. This global fitnessvector is then disseminated back to the nodes, each of which applies the same ES updateto be synchronized to the global model.Our experimental and theoretical analyses demonstrate that EvoFed achieves performance comparable to FedAvg and compresses the model more than 98.8\% on FMNIST and 99.7\% on CIFAR-10, reducing overall communication.EvoFed significantly reduces communication overhead and enhances privacy byproviding protection against eavesdroppers who do not participate in collaborative learning.These advancements position EvoFed as a significant step forward in FL, paving the way for more efficient and scalable decentralized machine learning.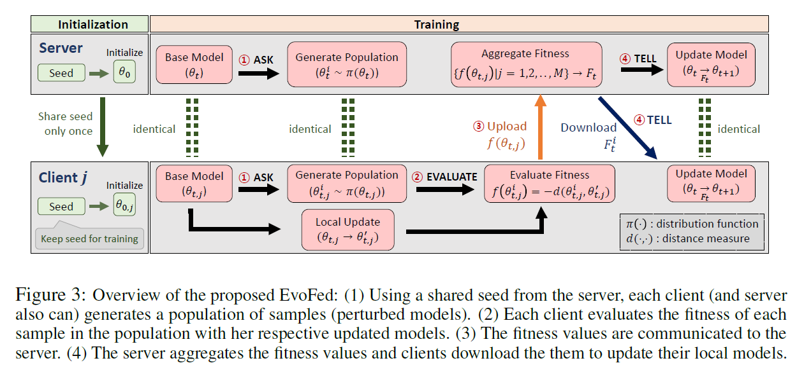
Authors: Jungwuk Park*, Dong-Jun Han*, Jinho Kim, Shiqiang Wang, Christopher G. Brinton, Jaekyun Moon (*=equal contribution)
Conference: Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS) 2023
Abstract:
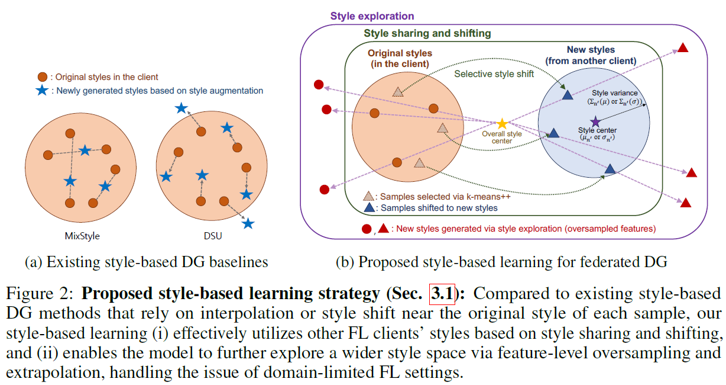
Traditional federated learning (FL) algorithms operate under the assumption that the data distributions at training (source domains) and testing (target domain) are the same. The fact that domain shifts often occur in practice necessitates equipping FL methods with a domain generalization (DG) capability. However, existing DG algorithms face fundamental challenges in FL setups due to the lack of samples/domains in each client’s local dataset. In this paper, we propose StableFDG, a \textit{style and attention based learning strategy} for accomplishing federated domain generalization, introducing two key contributions. The first is style-based learning, which enables each client to explore novel styles beyond the original source domains in its local dataset, improving domain diversity based on the proposed style sharing, shifting, and exploration strategies. Our second contribution is an attention-based feature highlighter, which captures the similarities between the features of data samples in the same class, and emphasizes the important/common characteristics to better learn the domain-invariant characteristics of each class in data-poor FL scenarios. Experimental results show that StableFDG outperforms existing baselines on various DG benchmark datasets, demonstrating its efficacy.
Authors: Seokil Ham, Jungwuk Park, Dong-Jun Han, Jaekyun Moon
Conference: Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS) 2023
Abstract:
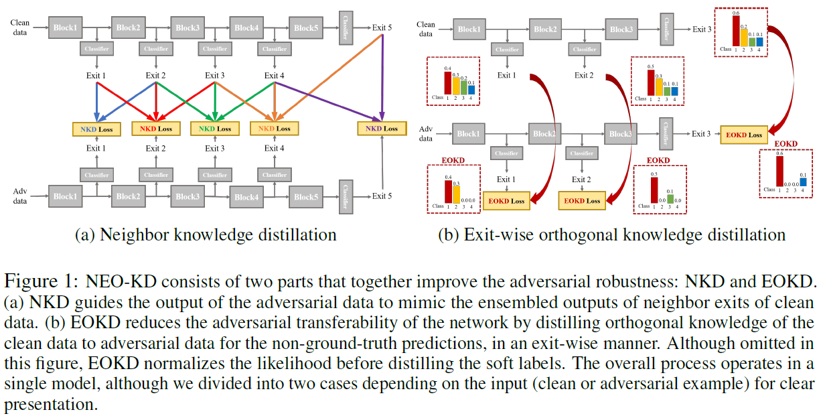
While multi-exit neural networks are regarded as a promising solution for making efficient inference via early exits, combating adversarial attacks remains a challenging problem. In multi-exit networks, due to the high dependency among different submodels, an adversarial example targeting a specific exit not only degrades the performance of the target exit but also reduces the performance of all other exits concurrently. This makes multi-exit networks highly vulnerable to simple adversarial attacks. In this paper, we propose NEO-KD, a knowledge-distillation-based adversarial training strategy that tackles this fundamental challenge of multi-exit networks with two key contributions. NEO-KD first resorts to neighbor knowledge distillation to guide the output of the adversarial examples to tend to the ensembled outputs of neighbor exits of clean data. NEO-KD also employs exit-wise orthogonal knowledge distillation for reducing adversarial transferability across different submodels. The result is a significantly improved robustness against adversarial attacks. Experimental results on various datasets/models show that our method achieves the best adversarial accuracy with reduced computation budgets, compared to other baselines relying on existing adversarial training or knowledge distillation techniques for multi-exit networks.
Authors: Dong-Jun Han*, Jungwuk Park*, Seokil Ham, Namjin Lee, Jaekyun Moon (*=equal contribution)
Journal: IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023
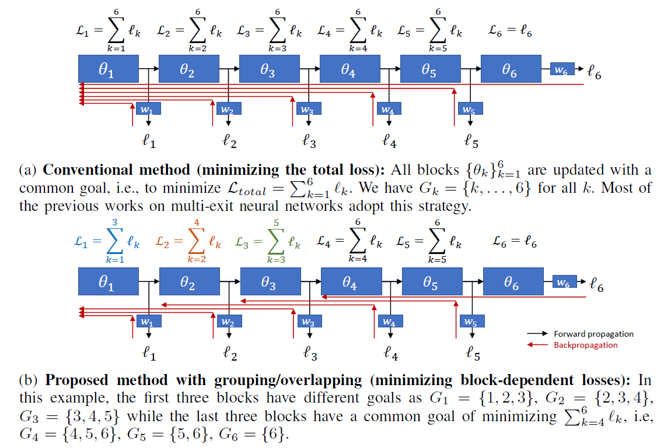
Abstract:
As the size of a model increases, making predictions using deep neural networks is becoming more computationally expensive. Multi-exit neural network is one promising solution that can flexibly make anytime predictions via early exits, depending on the current test-time budget which may vary over time in practice (e.g., self-driving cars with dynamically changing speeds). However, the prediction performance at the earlier exits are generally much lower than the final exit, which becomes a critical issue in low-latency applications having a tight test-time budget. Compared to the previous works where each block is optimized to minimize the losses of all exits simultaneously, in this work, we propose a new method for training multi-exit neural networks by strategically imposing different objectives to individual blocks. The proposed idea based on grouping and overlapping strategies improves the prediction performance at the earlier exits while not degrading the performance of later ones, making our scheme to be more suitable for low-latency applications. Extensive experimental results on both image classification and semantic segmentation confirm the advantage of our approach. The proposed idea does not require any modifications in the model architecture, and can be easily combined with existing strategies aiming to improve the performance of multi-exit neural networks.